Do-it-yourself summer greenhouses are the best projects. Ideas and ready-made solutions for building the cheapest greenhouses with your own hands
The dream of many is to have their own greenhouse on their own. suburban area. This design perfectly provides vegetables and herbs. all year round with a thorough approach to its construction.
The simplest greenhouse options are from frames and plastic pipes, designed for one season, are quite affordable without serious investment for construction on a personal plot.

Location selection
It is important from the very beginning to decide on the functions of the greenhouse. Will it be used only seasonally or all year round. The choice of its location and all subsequent financial costs for its erection will depend on this.

The most important thing in a greenhouse is lighting and maintaining the optimum temperature for seedling growth.

Therefore, if the greenhouse will not be used all year round, then you need to find a place for it on the south side, so that direct sunlight constantly falls on it, there is no shadow from the nearest buildings and trees.

If you plan to maintain a certain level of lighting and heating, then any place will do. In this case, you will have to spend money on heaters and various lamps to create an optimal microclimate inside the greenhouse.

You also need to remember about, so as not to overdry the nutrient soil, not to slow down the development of seedlings during a period of rapid growth.

The choice of material is an important point
Depending on the type of greenhouse, one or another material will be required for its assembly and installation. The main thing is that it is strong enough to withstand aggressive influences. environment: gusts of wind, heat, precipitation in the form of hail, snow and rain.

The design of the greenhouse is quite simple: a frame is fixed on the mounted foundation, which is then glazed, sheathed with polycarbonate, or a polyethylene film is stretched over it.

The foundation can be either deep underground, in a thoroughly dug pit (the so-called "thermos"), or of the same type as for other structures. Simple or complex. It all depends on the intentions, financial capabilities and the approach to business.

The most popular option is glass, reinforced or plain polyethylene. The more solid the structure, the more time, effort and money must be spent on its erection.

The frame itself can be made of metal, plastic, wood, from old window frames. Much depends on the available opportunities and imagination. Even from improvised means (the same plastic barrel) some craftsmen manage to build a mini-greenhouse.

Varieties of greenhouses
The design of the greenhouse is not complicated, any owner, with the availability of material and tools, is able to make it with his own hands. Such agrotechnical structures are various kinds- from simple, made from improvised means to more complex ones, with lighting, watering and heating.

Much depends on the purpose of creating a greenhouse. Will it be used for a whole year, or - seasonally, temporarily. The issue of its erection must be approached thoroughly and an appropriate site for construction must be selected.

Thus, greenhouses are:
- Simple, more reminiscent in appearance;
- Complex;
- Mobile (temporary, collapsible);
- Stationary;
- From cellular polycarbonate - from transparent to various yellowish, green shades;
- From glass;
- From a frame made of plastic (metal) pipes;
- From old window frames;
- With various form structures (arc, triangular, square);
- Type "thermos", placed in a dug deep pit.

Greenhouse cover
After a thorough erection of the foundation, the construction of the frame, it is time to think about what the greenhouse will be covered with. The durability, strength, and reliability of the entire structure will depend on this.

Many owners of summer cottages go the traditional way - they use glass to cover the walls and roof of the greenhouse. This kind of coating reliably protects plants from aggressive environmental influences - rain, frost, gusts of wind.

Significant drawback - big weight, load on supporting structures. Therefore, it is necessary to thoroughly approach the manufacture of the frame, so that later, with a gust of wind, accumulation of snow on the roof, the greenhouse does not collapse at once, does not destroy the seedlings.

The simplest, most inexpensive option is to use a polyethylene film. It can be either reinforced, more durable, or simple. We have a low weight, so the frame does not experience increased loads, it can be made of metal-plastic pipes, which bend well in any direction, are strong enough for this kind of construction.

Cellular carbonate of various shades favorable for plant growth has become very popular for covering roofs and walls. It also has a small weight, is durable, reliable, has good sound insulation and tightness.

In terms of use, glass and polycarbonate are durable. While the polyethylene film fades under the influence of ultraviolet, loses its ability to transmit sunlight, and collapses. If the greenhouse is designed for seasonal, temporary use, then such an inexpensive cover will do. If it will be used all year round, then the issue of choosing a coating must be approached thoroughly so that the plants feel good in the cold season and develop normally.

Design
As already mentioned, greenhouses are simple and complex. In terms of design features, they also differ from each other. Before proceeding to the decision to build any of its varieties with your own hands, you need to study in detail the available drawings and sketches in order to be aware of what you have to deal with.

In appearance, greenhouses are:
- In the form of a huge box, covered with old window frames or covered with polyethylene, from a simple arc frame, from metal-plastic pipes;
- Spacious, reminiscent of an elegant house, rooms;
- Receding half the height into the ground.

It is important to observe inside the greenhouse temperature regime, periodically water growing plants. Therefore, when the issue of construction is approached thoroughly, then at the planning and marking stage, it is determined in advance what lighting, heating, fertilizer and watering will be.

For small greenhouses designed for seasonal, temporary use, placement in direct sunlight is suitable, which will both heat and stimulate the growth of seedlings.

When it will be a separate building, then everything needs to be carefully thought out to the smallest detail so that in the cold season there are no unforeseen problems, the plants do not die.

Thus, when it becomes necessary to build a greenhouse on your site, you need to decide for what purpose, how often it will be used. The appearance, the cost of erection will depend on this.

Many go the simple way - they knock together a large wooden box, make a metal-plastic arc frame, and stretch a plastic film over it. Or - just cover it with window frames. This is the simplest, budget option.

More complex options require serious financial costs. But the greenhouse will eventually resemble a comfortable house in which plants can live around the clock for a whole year, delighting their owners with greenery and juicy fruits.
Photo examples of do-it-yourself greenhouses for summer cottages













































A greenhouse is an indispensable element in any summer cottage. Thanks to this relatively small but very necessary structure, you can provide favorable conditions for the rapid growth of seedlings, protect tomatoes and cucumbers, as well as other garden crops from frost, get an early harvest - the greenhouse will always take care of your plantings. It can be of any form, among which you can easily choose the one that suits you and your site best. At the same time, it is not at all necessary to buy this house for plants - you can make a greenhouse with your own hands quickly and easily if you know how.


Before you go to the barn to assess the availability of materials and tools or to the store to purchase them, you need to inspect garden plot and choose a place where the greenhouse will be built. Of course, the design can be portable, but most often it is made stationary. In addition, the size of the structure will depend on the choice of location and the availability of free space, and this factor greatly affects the amount of materials needed for construction.

A place for a greenhouse should be chosen according to the following principles.
- It must be a flat piece of land. Installation of the structure on steep slopes is unacceptable. If there are snags, stumps on the territory allocated for the greenhouse, then they must be uprooted, and all the pits should be covered with soil.
- Growing and fruiting plants need good lighting. That is why a greenhouse is not installed where a shadow from trees, shrubs, greenhouses, houses and other buildings falls on the ground. The lack of light will negatively affect both seedlings and adult crops.
- The gardener should be comfortable doing all the work in the greenhouse. Therefore, you need to try to calculate the location in such a way that there is a sufficient passage around the structure, and the greenhouse can be easily opened.


On a note! If the greenhouse is planned to be used for the permanent cultivation of plants, for example, then care should be taken to build a second greenhouse, if space permits. The fact is that it is undesirable to grow the same crops, especially tomatoes and cucumbers, in the same place from year to year. Plantings are usually interchanged. In this case, the second greenhouse would be very useful.

The best time to build a greenhouse is mid-spring. The snow has already melted, and the plants are not growing much yet. Although if there is nowhere to hurry, then you can build a greenhouse at any time of the year, except for winter. AT winter period it is very difficult to carry out any construction, not only because of the cold, but also because of the hard ground.

Greenhouse dimensions
In general, the size of any greenhouse depends entirely on the desire and capabilities of the gardener, as well as on the types of crops that will be grown in it. If a greenhouse is needed only for accustoming seedlings to the street, but not for its permanent place of residence, then it can be completely small or hastily assembled without any special material costs. But if this design is meant to be capital, then it is best to make some calculations so that later you do not get upset and do not shrug in case of a shortage or excess of space.
Calculations should begin with the development of a structure diagram (we will consider the types of greenhouses below). Thanks to her, it will be easier to calculate the necessary parameters and the amount of materials.
On a note! Usually they make greenhouses about 1 m wide and no more than 2-3 long. In this case, the height is approximately 50-60 cm. Such dimensions will be as comfortable as possible both for working inside the structure, and for growing seedlings, as well as undersized crops.
Also, the number of plants that will live in a greenhouse can be taken as the basis for calculations. For example, no more than 3 bushes of cucumbers or tomatoes can easily coexist per 1 m 2. Based on this, you can calculate the dimensions of the structure you need.
It is also important to consider the dimensions of the material that will be used to build the structure. Sometimes it's easier to make a couple of small greenhouses than one long one, which can only be obtained by joining the material.

Greenhouse types
Greenhouses for cottages come in a wide variety of forms. To decide what type your greenhouse will be, you should get acquainted with the main ones.
Table. Greenhouse types.
| Type of greenhouse | Description |
|---|---|
| A greenhouse that opens on the principle of an ordinary bread box. It happens factory or homemade. It is convenient because the lid does not strive to fall down and does not need props, unlike, for example, a "butterfly". |
| One of the simplest options for greenhouses. Several plastic or wire arcs are stuck into the ground along the beds and covered with spunbond or polyethylene. It is quickly disassembled and assembled, moreover, this process can be carried out by almost any gardener. |
| The lower part of this structure - the base - is recessed into the ground, only the cover of the greenhouse is on the surface. This way of arranging a house for plants allows you to keep warm longer inside the structure. |
|
| The greenhouse is arched or a house, has two wings that open outward. It can be produced at the factory and made by hand. Provides uniform access to plantings from both sides. |
| One of the simplest types of greenhouse is two battens connected in a “ridge” and covered with polyethylene or other material. It is mounted quickly and simply, but is unstable and is used more often as a temporary portable structure. |
Each of the above types has certain variations, supplemented by one or another element. For example, an ordinary greenhouse-bread box can be installed not on the ground, but on the base, thereby making it higher. There are also a lot of greenhouses - for this, ordinary sports hoops, window frames, headboards from beds and much more are used. Sometimes it’s enough to rummage in the shed in the country, where unnecessary things are stored, and find a few items that can easily get a new life in the form of a greenhouse frame. All it takes is a little skill and imagination.




Greenhouse materials
It's time to discuss the main types of materials from which it is easy to create a greenhouse with your own hands. The frame itself can be of three types.
- Metal. This material is the most long-lived and durable compared to others. He is not afraid of wind or snow. Metal arches can withstand a greater mass than plastic or wooden ones. Metal has two main drawbacks - complexity in processing (certain devices are needed to work with it) and a tendency to corrosion (this drawback is corrected if the frame is painted). Also, in the event of a greenhouse falling, the metal base will simply crush the plants.



After the construction of the frame, it must be covered with a covering material that will retain heat and protect the plants from wind and cold. Consider the possible options.
- Glass. Heavy, but high-quality and durable material with increased fragility. It is easily damaged by impacts, breaks when dropped, but does not bend, and therefore can only be used for greenhouses with even walls. Does not retain ultraviolet and retains heat worse, difficult to process.
- Polycarbonate. Recognized as one of the best covering materials. It has a certain strength, it is not afraid of moderate wind / snow loads, it bends perfectly, and therefore can be used for the construction of curved structures. The material has protective layer, which prevents the penetration of ultraviolet rays into the structure, and due to the honeycomb structure, it perfectly retains heat. The service life is shorter than that of glass, but in some ways the material is even stronger, because it is not so fragile and will not break if dropped from a small height. Polycarbonate is also very easy to process.




Cucumbers are demanding on growing conditions and give good harvest only at stable air and soil temperatures. Providing cucumbers with the right microclimate is quite simple: you need to install a major or seasonal greenhouse in the garden. We will talk about how to make a greenhouse for cucumbers with our own hands in.
Also, to connect individual elements, you may need corners, self-tapping screws, washers, corner profiles, clamps. For the convenience of opening greenhouses with doors, handles and canopies are used.

Prices for cellular polycarbonate
cellular polycarbonate
Greenhouse "house"
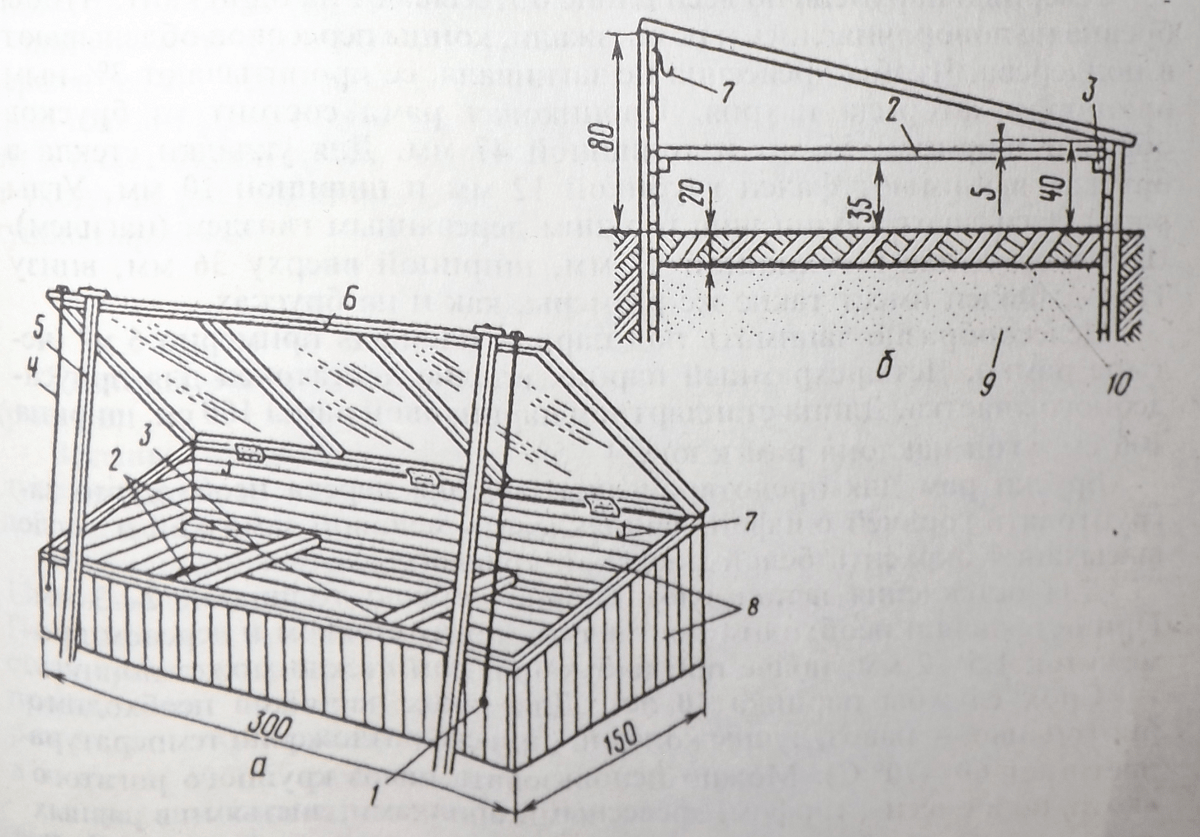
A gable portable greenhouse is one of the simplest options that you can build yourself. It is a "roof" with two slopes, placed on the ground and covered with a film. You can make it easily and quickly from a wooden beam of about 5 * 5 cm, metal corners and self-tapping screws or nails.
Step 1. We create two frames by connecting the bars with each other, equal in length to the length of the greenhouse, and shorter.


Step 3 We connect the two frames to each other in the upper part with the help of a ridge rail. The approximate angle of connection is 90 degrees.

Step 4 At the bottom of the frame we connect the elements with longitudinal rails. We've got a frame.

Step 5 Now the frame must be covered with a film so that it can rise to ventilate the plantings. To do this, we cut off the piece of covering material we need, slightly longer in length than the sum of the two side parts of the greenhouse.

Step 6 We cut out two pieces of polyethylene triangular in size the same as the sides of the frame. We pin them with small carnations on the sides.

Step 7 We pin a large piece of polyethylene along the ridge rail.
Every summer resident and owner of his own house, sooner or later, has a desire to have a good greenhouse on his site. After all, everyone knows that vegetables and herbs from their own greenhouse, also grown with their own hands, are much tastier and healthier than purchased ones. Therefore, someone follows the path of buying a finished greenhouse. Someone buys a disassembled greenhouse and assembles it on the site as a constructor. But a considerable part of gardeners want to build a greenhouse with their own hands. After all, everyone knows: if you want to do something well, do it yourself.
How to build a greenhouse with your own hands? To begin with, let's figure out what types of greenhouses are. This is important for choosing the future design and material of the greenhouse.
Winter and summer greenhouses
All greenhouses can be divided into two large groups: winter and summer. They differ in the presence of a heating system in a winter greenhouse, which allows you to grow plants in such a greenhouse all year round. The summer greenhouse is designed for faster ripening of fruits and protection of plants from accidental frosts.
Winter greenhouses are usually more solid than summer ones. They build them closer to the house, sometimes even attaching them to the south side of the house. So they are closer to the heat source. Winter greenhouses are almost never made from film. The heating system can either be connected to the heating system of the house or be autonomous. For this, an oven is made in the greenhouse.
Video review of a self-heating winter greenhouse
Arched, single-pitched and double-pitched greenhouses
Everyone chooses the type of roof for the greenhouse based on the location of the greenhouse. As well as your personal preferences. We can only suggest the advantages and disadvantages of each of them.
shed roof they usually choose by attaching a greenhouse with their own hands to the house. This type of roofing is simple in construction, economical. Under such a roof, you can make an inexpensive, but solid base of a wooden beam or metal profile pipe. The disadvantage of this roof is that snow will accumulate on such a roof.

gable roof, like a lean-to, it can have a cheap and durable frame. It is a little more expensive than a single-sided one, but more aesthetically pleasing. But snow will also accumulate on such a roof. Consider this factor when choosing a roof for a greenhouse.
Types of greenhouses. Video review
And finally arched roof. A very popular type of roofing and deservedly so. Economical, quickly built, he won his niche very quickly. In combination with cellular polycarbonate, such a greenhouse has almost all the advantages. It does not collect snow, it is very resistant to winds and the dispersion of sunlight in it occurs naturally. The only drawback may be a frame for this type of roof. Making a strong and reliable frame will be more expensive and more difficult than for previous types of roofing. Let's talk about frames for greenhouses with our own hands.

Types and materials for the frame of the greenhouse
We continue to answer the question of how to build a greenhouse with your own hands. If you decide to build a greenhouse on your site, have chosen the type of roof for your future greenhouse, now you need to think about choosing a material for the greenhouse frame. What to build a greenhouse from?
The greenhouse frame can be made from:
- tree
- metal
wooden frame
Timber frames are very easy to work with. The tree is easy to process, it can be used to build a greenhouse of almost any kind. The disadvantage of such construction will be the susceptibility of the tree to decay. Therefore, the entire timber before construction has to be treated with special impregnations.

Greenhouse made of wood and film. Video building instructions
Metal
In order to assemble a metal frame, good skills are needed. After all, the metal will either have to be welded or bolted. Such a frame for a greenhouse is very expensive. But it is very durable, reliable and will last for decades. Such a frame is suitable for a capital greenhouse.

Video of building a glass and metal greenhouse
Plastic
Today, the construction of greenhouses from plastic pipes is gaining popularity. This type of construction is relatively cheap, even beginners can do it. Moreover, such a construction will not take much time. The disadvantage of such a frame is its low strength. Over time, plastic pipes bend, the greenhouse loses its shape. Therefore, as a capital structure, such a frame is not suitable.
Video how to make a greenhouse from plastic pipes and film
Greenhouse cover
The materials for the walls and roof of the greenhouse are very diverse. Each has its pros and cons. Let's look at them in more detail.
- glass
- film
- agrofibre
- cellular polycarbonate
DIY glass greenhouse
How to build a greenhouse with your own hands? If you want to build a capital and durable greenhouse with your own hands, then a glass greenhouse a good option. Moreover, such a greenhouse will not necessarily be expensive. After all, it can be built from.

Many people, changing old wooden windows on plastic ones, they just throw the frames in the trash. So you can get the material for your greenhouse for free. You just have to process the wood of the window frames and fasten them together. You will even have windows and vents ready to ventilate the plants on hot days.
Video review of a greenhouse from old window frames
However, do not forget that glass is a heavy material. Therefore, the foundation of such a greenhouse should be appropriate. It must be recessed, or . Or you can do slab foundation and take water out of it.
DIY film greenhouse
Such a greenhouse, although it requires frequent film changes, is still common. Because the film is easy to mount and it is cheap. In addition, with careful attitude, it can withstand several seasons. It is not suitable for a do-it-yourself winter greenhouse, but it copes very well with the functions of a summer one.

An ideal design option for a film greenhouse would be a frame made of plastic pipes curved by an arch. Such an arch is built in one day, it is cheap and even one person can handle it. The arch is closed with a film. And for the winter it can be removed. It is possible to modernize such a greenhouse somewhat if agrofiber (geotextile) is used instead of a film.
Do-it-yourself agrofibre greenhouse
Can be used as a do-it-yourself greenhouse covering material. It passes water and steam well. Your plants will be irrigated with rainwater and will be able to "breathe" freely. White geotextile provides enough light for plants, and at the same time will not let the sun's rays burn the foliage. Such a greenhouse needs less ventilation than those made from other materials. Agrofibre is a durable material, unlike film. You can use it for many years. It does not tear, is not afraid of piercings, stretches well. Today, this is a good alternative to film.
Step-by-step video instructions for making agrofiber greenhouse
Do-it-yourself cellular polycarbonate greenhouse
Do-it-yourself such greenhouses are made for all types of roofs and frames. They are both arched and single-gable. Polycarbonate is attached to both wood and metal. They are covered with frames made of plastic and aluminum pipes. In general, this is a universal material for building a greenhouse with your own hands. When choosing polycarbonate, pay attention to its thickness and weight. Choose sheets with a thickness of 4 mm. Better than 6-8 mm. In addition, the sheet should be heavy enough. Do not forget that polycarbonate cannot be mounted in a horizontal position. The condensate in the combs must be free to roll and flow out. Otherwise, polycarbonate will quickly become overgrown with algae and lose its transparency.




How to make a polycarbonate greenhouse on a metal frame. Video
We hope that our article helped you in choosing the type of your future greenhouse and we answered the question of how to build a greenhouse with your own hands. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments to the article. We are very interested, but what kind of greenhouse did you make with your own hands?
Can be assembled with minimal effort. Therefore, today we will discuss best ideas how to make greenhouses with your own hands. Most best projects we will show in photosets and master classes.
The first and most important thing, how a greenhouse differs from a greenhouse, is the lack of heating in the winter. The greenhouse structure is purely seasonal. However, in southern regions, where the temperature is above zero all year round, greenhouses are constantly used.

There are several varieties of them. The most popular and easy-to-make greenhouses of the "Agronomist" type. Although such structures have different names, the design variation does not change - a simple low frame made of plastic pipes or wood, dug into the ground. On top of this design is covered with a film. Frames are made for reinforcement.


More "serious" designs are greenhouses with a sash opening mechanism. There are several varieties -, "Chest". All of them are shown in the photo below.




Also popular among gardeners are full-sized greenhouses for growing tall plants seasonally. Outwardly, they resemble greenhouses, but the main “ingredient” is missing - the heating system.
Related article:
Standard dimensions, what the design is, its advantages and disadvantages, the materials used in the manufacture, the features of the independent development of the drawing and the assembly of the polycarbonate greenhouse - read our publication.
Overview of winter greenhouse projects for do-it-yourself construction
In fact, you can make heated greenhouses and for giving your own hands, you can absolutely any configuration. The main thing is that there should be a complete tightness of the structure and be present. Also, another condition is the arrangement. It is desirable that it be monolithic and raised above the ground by at least 15 cm.

best material the cladding of such greenhouse structures is glass or polycarbonate, which is more affordable and easy to process. At the same time, it keeps heat indoors more efficiently, which can also lead to stale air. Therefore, even at the design stage, it is necessary to think over not only the heating system, but also for the winter period.
Overview of the best projects for a do-it-yourself greenhouse heating device
The first thing to know about heating a greenhouse with your own hands is that not only warm air is important for plant growth. Therefore, the best projects involve ground heating, which will also provide more comfortable conditions. Consider what are the options for heating greenhouses:
- - the simplest and most economical heating system in the device. Great for ground heating. But his device is more suitable for buildings located near the main house.
- Electricity- a very expensive way of heating, if we consider it in a variation of the heat supply from. Another thing is if a pump organizes a heating system that works with water, soil or air. If there is a body of water nearby, then it is best to use the “water-water” scheme. "Soil-water" is the most expensive option, but also effective. “Air-water” is cheaper, but it is tied to climatic conditions. In frosts from -25 ° C, the system fails.
- Gas- Another common method of heating greenhouses. And the cheapest, which may not seem at first glance. But there is one caveat, when heated with gas, a large amount of carbon dioxide is emitted, so there is a risk of burning the air. Therefore, the system is always arranged for .
- biofuel- the most economical and easiest way to do-it-yourself heating. In the process of decay, heat is released, which is necessary for the growth of plants. Humus is simply laid under the ground, and after a few months it is updated. True, in the northern regions of the country this method is not enough. You can use it for small areas of greenhouses.
How to choose The best way heating a do-it-yourself greenhouse, the video below will tell you.
What is the "skeleton" of greenhouses and greenhouses made of?
Frames for both greenhouses and hotbeds are made of the same materials:
- Wood- not the cheapest option, but reliable with proper design and processing. So that the frame does not rot, it is necessary that the tree does not come into contact with the ground, it is about 30 cm higher above it. Painting and varnishing is also required. But remember that wood is still an organic material, which in a couple of years will shrink, dry out, and you will have to produce repair work. Slowly moving away from the role of the main frame material for greenhouses and greenhouses.
- Metal- a more reliable option for the frame. Apply both strips and profiles, painted or galvanized. Minus - the severity of the frame and the obligatory device of a good one. Perhaps the most expensive material for the frame of the greenhouse system.
- plastic pipes- relatively recently began to make various items and spatial figures. As the main frame material for greenhouses and hotbeds, such pipes have shown themselves well - they are easy to process, light in weight, flexible, and the ability to manufacture even complex structures. They also need a foundation and additional reinforcement of the structure. Of the minuses, it can be noted that only films and a maximum of polycarbonate can be used as a covering material. Glazing such a frame simply will not withstand.
You can buy a polycarbonate greenhouse only with metal frame. Manufacturing enterprises do not make such structures from pipes. This is the fate of perhaps "handy gardeners."
Polycarbonate is an ideal material for making simple greenhouses and winter greenhouses with your own hands.
A polycarbonate greenhouse today is incredibly popular. How did such material deserve people's love? There are several reasons why you should choose, which the video after the description will also tell about:
- a honeycomb structure filled with air makes polycarbonate a heat-retaining covering material;
- light transmittance;
- flexibility - you can sheathe a frame of any shape;
- accessibility of installation - easy to self-processing and installation on simple fasteners - self-tapping screws, bolts;
- durability - the service life can be up to 20 years;
- not exposed to atmospheric influences;
- resistance to mechanical damage;
- relatively inexpensive material.
Is polycarbonate the ideal building material? No, as we know, everything in this world is imperfect. One of the main disadvantages is flammability, under the influence of fire, and simply high temperature, it begins to melt.
Also, professionals in crop production, despite all the seductive advantages of polycarbonate, try to bypass it due to its high reflectivity. If there is one, then less light will pass inside. If this is not critical for greenhouses, then for professional greenhouses it is a real disaster.

Also, polycarbonate does not "breathe" at all. This, of course, is a definite plus - a stable warm and humid microclimate develops inside the greenhouse, as plants love. But, on the other hand, they also vitally need fresh air in any weather. This problem is solved by installing vents and others, walls and doors. However, if such a greenhouse is not opened for a long time, then the plants there can simply die from stuffiness.

Polycarbonate is a popular type building material with a wide variety of species. And not every type is suitable for sheathing a finished structure. What you need to pay attention to:
- Only honeycomb sheets are suitable, since they retain heat better due to an additional air gap, which is not present in a monolithic material.
- Also pay attention to cells. Usually they have a square shape, but it is better if each of them also has a diagonal partition, which provides additional rigidity to the sheet.
- It is also better to give preference to the usual transparent material, since it has the largest percentage of light transmission. Colored sheets can absorb it by 60%, which will only destroy the plants in the greenhouse.
- Be sure to pay attention to UV protection, as prolonged exposure to the sun can warp polycarbonate. If the manufacturer claims that it is, but only inside, this means that its level is minimal. Sheets on which there is a protective film, with the recommendation of the manufacturer of mounting the sheet with a certain side outward, are the guarantor of the protective layer.
- Optimum thickness for the device, both greenhouses and hotbeds various modifications, - from 4 to 10 mm with a lathing step of 700-1050 mm. These are the optimal characteristics that allow you to build reliable structures.
- Also great importance when choosing such a material, its specific gravity plays a role. The greater the weight of the sheet, the higher its density, which means that the strength will be greater. The optimal density is from 0.7 kg / m 2.
- High-quality material does not allow any, even the smallest defects on the surface. Also, the stiffeners should go strictly in straight lines, no waves or zigzags.
- If the sheets were stored correctly, it means that their quality percentage did not fall. Proper storage- the location of even sheets in a horizontal position. If the polycarbonate was on edge or wrapped in rolls, it is better not to take such material.
Related article:
. Dimensions, prices of products from leading manufacturers, characteristics, varieties, pros and cons of different designs, features of assembly and use, user reviews - read our publication.
The foundation is the head of everything, or when you need a foundation for greenhouses and greenhouses
The foundation sounds proud and solid. But is it needed when arranging greenhouses and hotbeds? It depends directly on the type and size of the structure. When building a mini-greenhouse, for example, "Khlebnitsy", laying the foundation is not required. Someone just puts such a structure on the ground. But this is not always advisable, since such polycarbonate structures are relatively light in weight. Therefore, it is recommended to mount it on, which, if necessary, are dug into the ground. Small ones are improvised, and are completely mounted without a foundation. For structural rigidity, it is preferable to “mount” the arches on pre-dug ones.

Today at the peak of popularity are growth arched greenhouses made of polycarbonate. In fact, the weight of such a structure measuring 3 × 6 meters is 100 kg. This means that approximately every square meter structure is subjected to a load of 10 kg. By construction standards, this is just a “ridiculous” load, which is not even taken into account in the calculations. But guided by the unpredictable climate of our country and the experience of summer residents, such greenhouses are blown away by a good gust of wind. No, not to the Emerald City, of course, the maximum to the neighboring site. But such an unplanned flight can cause a lot of damage. Therefore, when constructing large greenhouses, it is best to make full-fledged foundations on or sand blocks.

And, of course, a solid foundation is simply necessary for stationary greenhouses. Firstly, it will remove the load and distribute it evenly throughout the structure, which guarantees a longer service life. Secondly, even during a hurricane, the building will remain in place. And, thirdly, the foundations prevent the freezing of the soil, additionally the soil. Bases are made from those materials that are convenient to work with, and even more economical in a particular case, bricks, blocks, concrete monolith or tape, and even screw piles.



Attention! The type of foundation for greenhouses is chosen in the same way as for the main buildings - primarily by the type of soil.
Article
If you want to diversify your personal diet, moreover, please the family with real natural vitamins before the next seasonal harvest appears, and with the right approach, to deliver fresh berries and vegetables to the table throughout the year, it is optimal to purchase a greenhouse or greenhouse from us, and if you have certain skills and free time, you can build a greenhouse or greenhouse yourself. How to make a greenhouse or greenhouse yourself?
Of course, before you get down to business, you should think through the various parameters and nuances of the potential process, thoroughly understand the question of how to create a greenhouse with your own hands:
- you need to decide how much area of the site can be free;
- to resolve the issue with the functionality of the design, that is, the greenhouse will be relevant throughout the year or will be used only in the spring. The year-round option needs a lot of effort and materials, because you will have to additionally conduct heating, lighting, water and equip high-quality ventilation;
- then the type of structure and the materials from which it will be built are determined.
In order not to miscalculate in this case, it is better to consider variations of greenhouses and greenhouses.
Varieties of greenhouses and greenhouses
Now there are many modifications of greenhouses and greenhouses, moreover, based on general principle their arrangement, craftsmen create personal options, sometimes individual details for a given agrotechnical structure. Greenhouses are usually divided according to different criteria, for example, according to the forms and materials of release, stationarity, and also the time of construction.
Features of the design of the greenhouse and greenhouse
The frame of a greenhouse or greenhouse is usually made of boards, and the useful volume is formed thanks to the lid in the form of glazed frames, they can be opened if necessary. This solution is optimal for growing seedlings, greenery, so that all this appears on the table as early as possible.

A temporary type of greenhouse, installed only for the period from spring to summer, is considered a combination of a wooden frame, plastic film, and fiberglass reinforcement. This solution will last for quite a long time, if the structure is disassembled into parts in winter, and everything is stored indoors. As a result, you will simply change the film for a new canvas, it is not difficult and not expensive.

Some craftsmen mount a greenhouse in a large old barrel, it is also used in the spring, but it is not necessary to remove it from the site in the winter, because the design can serve as a flower bed, or even an open garden bed.

Another solution needs forced heating, and is used immediately after the snow has melted. The structure is made of boards, metal-plastic fittings, covered with plastic wrap, and in order to look after the plants, it will be possible to go right inside.

The capital greenhouse is equipped with various necessary details, a certain microclimate is created inside it, which guarantees the operation of the building throughout the year. To do this, it is enough to make a not very deep foundation, then a brick base, and insulate everything well.

Such a greenhouse can even be attached to one of the walls of the living space, then it will be easier to connect the system to communications. It is comfortable to take care of the plants throughout the year if an exit to the greenhouse from the house is equipped.

In order to save on heating in the winter season, you can install a kind of thermos greenhouse, for which they dig a foundation pit, the depth of which is 1.7-2 m, then everything is covered with a transparent roof. The solution is interesting, but the main thing is to take care of the ventilation system. Of course, this option is laborious in its own way, but as a result, the design guarantees savings in energy costs.

What should be the shape of the roof?
Before you make a greenhouse or greenhouse with your own hands, you need to determine its shape, in no case do not forget that you still need to install a roof, and this is an effective detail in growing plants. Most popular solutions:
- gable roof, greenhouses of this kind are in demand, because they are really spacious, comfortable to be, moreover, both for plants and gardeners. With the right design, installation and choice of material, the room will be illuminated by sunlight throughout the day. Such a plan is equipped with greenhouses under winter gardens, planting them not so much with vegetables, but with exotic plants. Of course, this option will be realized only when the proper conditions are organized, there are reliable heating systems, lighting and irrigation;

- arched roof, this solution for an arched greenhouse is extremely easy to install when compared with a gable counterpart. The bottom line is that the form, closed with polycarbonate, as an option - with plastic wrap, ideally scatters sunlight around the room, so the plants will receive maximum natural heat. Also important point in this case, that due to the arc different shapes precipitation in the form of snow does not remain on the roof, that is, it does not deform or be damaged due to the increased load in the winter season;

- a shed roof is ideal for greenhouses that are adjacent to a massive building, for example, a house, or even a large stone fence, always on the south side. It is really possible to save money on the construction of this greenhouse, because one of its sides will be finished wall, the basis will actually adjoin to it. In addition to all that has been said, it will be extremely simple to conduct communications in the greenhouse. Designing a greenhouse shed roof, you should choose the slope of the slope correctly, only in this way the snow will not lie on the surface of the roof, because the increased load will only damage the coating.

The main material for covering the greenhouse

When we make a greenhouse at home, you need to understand that for certain greenhouse designs you need different materials, but usually they are united by one feature - the material for covering the walls, as well as the roof, must be transparent, allowing enough light to pass through.

The table below contains information on the current physical, as well as technological, moreover, performance indicators of the three most popular materials. Namely, polycarbonate, polyethylene film, also classic silicate glass.
| Technical and operational parameters | Cellular polycarbonate | Glass | Film |
| Installation complexity and weight | Lightweight, self-supporting material. It makes it possible to reduce the number of frame parts and even completely abandon the foundation. | Glass is a heavy material, therefore, if it is chosen for coating, the building must have a solid frame and a reliable foundation (foundation) | A very lightweight material that needs to be securely fastened to the frame. |
| Durability | The operational period of the coating, proven by practice, is about 20-25 years, the manufacturer gives a guarantee for 10 years of its service. Polycarbonate, due to its rigidity, is itself an element of the load-bearing structure. Once fixed, it does not give deformation and distortions. | The material is durable if it is protected from the mechanical impact of heavy loads (snow and hail). | The service life of the film is very short, at best - 2-3 years, as it is destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet rays. |
| Noise isolation | The material, thanks to its honeycomb structure, suppresses wind noise well. | With poor-quality installation, the wind can penetrate the greenhouse, and the glass can make a ringing or rattle. | It almost does not create sound insulation, and in strong winds, it rustles in the wind itself. |
| Appearance | The aesthetic and modern appearance of the material creates a greenhouse even in some degree decorative element of a suburban area | Glasses have a fairly neat appearance if installed according to all the rules. | The material looks neat only in the first year after it is fixed, then the film becomes cloudy and collapses, especially if it is left on the frame for the winter. |
| Security | Polycarbonate is safe, does not break when dropped. It is 200 times stronger and at the same time 15 times lighter than fragile and rather heavy glass. | Glass shards are very dangerous if they hit the ground, as they can cause serious injury. Therefore, for safety reasons, glass installation must be carried out with strict observance of all safety rules. | In terms of injury, it is completely safe. |
| Care | Dust is almost imperceptible on the surface of the material, and if it is heavily soiled, it is enough to wash it with water from a hose. | Raindrops can linger on the surface of the glass, and then, when dried, they leave muddy marks. To wash off these stains from the surface, you will have to make a lot of effort. | It is not recommended to wash the film, as it will leave cloudy stains that will prevent the penetration of light. |
| Created microclimate | Polycarbonate perfectly insulates the room. The drops formed as a result of condensation of ascending vapors flow down the walls of the greenhouse, and do not fall on the plants or on the gardener's head. The material transmits and diffuses sunlight very well. The heat released by plants and soil does not escape through greenhouse covers, and therefore the necessary greenhouse effect is formed. | Glass does not provide the same high thermal insulation as polycarbonate, so the greenhouse effect is significantly reduced. The material transmits light well, but does not scatter it, and low-quality glass often starts to work like a lens, which is undesirable for plant leaves. | The new dense film creates good thermal insulation, but after working for one season, it becomes thinner and cloudy, therefore it loses its ability to completely retain heat and transmit light. |
Taking into account the indicated parameters, it is possible to determine best material for a specific greenhouse or greenhouse, which will be more consistent with their design.
Careful preparation for the construction of a greenhouse, its placement on the site

In order for planting in a greenhouse to find the light necessary for development, moreover, it receives it throughout the day, it is necessary to properly distribute and orient the structure on the site. The final harvest largely depends on how long the beds will be illuminated with natural light. For this reason, it is customary to install greenhouses in open space, as an option - with a transparent plane to the south.

Having decided on the type of greenhouse or greenhouse, and having found the optimal place for it on the site, plus, having distributed personal strengths and capabilities, you can proceed to drawing up a sketch, and also a small drawing.
Greenhouse or greenhouse design

It is not at all necessary to draw every detail under the ruler, given the strict rules of drawing art. If you are the owner and want to do everything on your own, the project is intended for you and your assistants, you can simply draw a greenhouse by hand in a projection in which it is possible to consider all sides of the building, then indicate the dimensions of the main details on them. Marking is usually done thanks to a rope and pegs, they are simply driven in along the perimeter of a potential pit.
What you need to know about the foundation pit and the foundation?
If you opted for a thermos greenhouse that will function throughout the year, then before digging a pit, it is optimal to carefully remove the top fertile soil layer from the territory. This soil is transferred to an individual pile, then it will be laid in the beds of the greenhouse. When deepening the pit, suddenly there are layers of clay located under the fertile base, it is also better to put it aside, separately from the mixed soil.

Clay will justify itself when adobe bricks are produced, they will be able to insulate the greenhouse. The depth of the pit should reach at least 1.7 m, but most often it is deepened to 2 m. It is at this distance that natural geothermal heat is stored that comes from the ground, so the soil never freezes. Naturally, if the greenhouse is not equipped in the northern regions of the country, there is always permafrost even at a shallow depth.
As for the width of the pit, the optimal figure is 2-5 m, and the length is determined based on desire. You can’t make the greenhouse wider, because it will quickly cool down, heating and lighting will require a huge amount of electrical and other energy. Not counting the pit itself, a smooth descent is made, as a result, an entrance door to the greenhouse will be installed there. If the place is marked for the all-season version of the greenhouse, it is optimal to dig a trench for the strip foundation, up to 0.3 m wide and deep.

This is really enough, since the structure is not heavy, so there is a minimum load on the foundation. In height, right above the ground, it is optimal to raise the foundation by 0.2-0.5 m, although sometimes only 0.1 m is poured, the rest of the wall is built of brick if necessary. Then sand is poured into the trench and rammed with a layer of 0.5-0.7 m, then crushed stone with an identical layer. After that, along the trench, with a small recess in it, formwork is installed, which as a result is filled with concrete mortar. It should be ensured that the concrete lies tightly and there is no air in it, in order to avoid problems, it is optimal to carry out bayoneting by piercing the poured mortar with a bayonet shovel.

Sometimes it happens that support posts made of metal pipes are embedded in the foundation, and other parts of the greenhouse or greenhouse will eventually be attached to them. It is possible that a wooden frame made of timber can become the basis for the greenhouse, it is treated with an antiseptic, installed on a sand cushion. 
Installation of greenhouses
Everything is clear with the base, you can proceed to the installation of the option you like.
Greenhouse or greenhouse on a wooden frame
A greenhouse that does not need a concrete foundation, where a solid wooden frame acts as the basis, is mounted without much difficulty:
A base box made of timber, with a section of 20x15 cm, is laid on a smooth prepared area covered with sand. The base should be in close contact with the surface of the earth over the entire area. For this reason, if a gap appears between it and the surface when laying the frame, it is better to close it with a stone lining. It is imperative to align the frame, otherwise the greenhouse will be uneven, its work will be unstable.
After you level the box, at its inner corners you need to drive pieces of reinforcement into the ground, the length of which is 0.7 m, this measure is important in order to fix the base in one place.

The next stage is the driving in of reinforcement along the long side of the box, moreover, 0.7-0.8 m should go into the ground, and 0.6-0.7 m should remain on the surface. The reinforcement should be at a distance of 0.5-0.7 m from each other, moreover, opposite rods similar to themselves, installed on the other side of the box, since this is the basis for fixing the pipes.

Pre-prepared metal-plastic pipes of the required length should be put on the surface of the reinforcement. A certain arcade is formed, which will serve as the basis for a transparent coating.

In order for the pipes to stand in one place tightly, it is better to strengthen them with metal loops that are screwed to the box with self-tapping screws.

If the structure is voluminous, it is better to strengthen it well on the end sides, they should stand rigidly. This frame not only guarantees rigidity, but also forms a doorway.

To do this, you need to vertically put the bars, the cross section of which is 5x5 cm, then fasten everything with horizontal crossbars in several places. Sometimes assuming that transverse fasteners are indispensable, pipes for arches are connected with cross adapters, horizontal sections of pipes are installed in them.

Another option for giving the structure full rigidity is to fasten the arcade at the top of the vault with a single pipe.

Fastening can be done with wire or plastic clamps, construction tape or "ties".

The frame, which is formed from pipes, must be covered with a dense plastic film, it is laid out with an overlap of 0.2-0.25 m. In the lower part, the film is attached with construction brackets and a stapler to a wooden box. Initially, the film is well stretched onto the arcade, then attached to the end sides, at the door the material is folded inside the greenhouse.

The door itself should be light, but be a rigid structure. It is usually created from a bar of 0.5x0.3 m, plus, in order to exclude deformation, a pair of battens is attached diagonally. Then the resulting canvas is covered with a plastic film. The door is usually hung on a pre-prepared opening due to the hinges. Just like this detail, window openings are installed, they are located almost under the ceiling, on the opposite side from the door. Thus, a natural flowing air circulation will be obtained.

Features of the thermos greenhouse
Building foundations for walls
After the foundation pit is ready for the greenhouse, a strip foundation is created around its perimeter. For this, a trench is necessarily pulled out, then various actions are carried out, identical to those described earlier, where it was a question of the foundation for a winter greenhouse.

When the foundation is completely ready, the walls begin to be laid, we must not forget about installing one or two ventilation pipes. They are installed at the bottom of the end side of the building, opposite front door, at a height of 0.5 m from the floor.
After installing the roof, it is customary to raise pipes to a height directly above the ground, at least 1 m.

Proper wall laying
The masonry of the walls is usually made from adobe, foam concrete blocks, sometimes from fixed formwork made of polystyrene foam blocks, their cavities need to be filled cement mortar. If the latter option is most relevant, you can immediately get insulated walls, but in this case it is valuable to separate the structure from the ground with plastic wrap. As soon as the stone walls are erected, the gap between the soil and the masonry should be sealed with clay, while ramming it well. The scheme of the greenhouse-thermos is clear in the lower figure.

The walls must be raised from the foundation above the ground by at least 0.5-0.6 m. If they were not used fixed formwork, then it is optimal to insulate everything to the depth of freezing of the soil, taking into account the regional climatic conditions where the greenhouse is set up.
Insulation can be installed with outside walls, that is, between it and the ground. For this reason, the gap between them will have to be expanded, then the insulation should be separated from the ground thanks to the waterproof film. When polystyrene foam acts as a heater, it will rise above the soil surface, in particular, from the outside of the building, while it is valuable to waterproof everything, then seal it with an outer decorative coating. It is optimal if it turns out to be a material that does not rot when moisture gets on it. For example, a plastic lining is suitable.
It is possible to close the insulation using a different method, for example, to cover everything outside with expanded clay, to cover it with roofing material from above. In this case, corrugated board is justified, it is fixed below polycarbonate, and even glazing. In this case, a plastic film for covering the roof will justify itself.
Frame installation
The next step will be the installation of the frame under the wall covering, and also the ceiling, with polycarbonate, because its installation is simple and safe.

Initially, on the walls that are raised from the pit, the bars are laid and fixed with anchor fasteners, their section size is literally 10-15 cm.

The rafters, as well as the ridge beam, should have a similar cross-sectional size as that of the bars mounted on the walls. A rare crate is attached to the rafters, literally 2-3 bars per slope. In this case, it is needed to guarantee the rigidity of the structure. Then sheets of polycarbonate are attached to the crate. They are hooked with certain self-tapping screws with a large cap, in other words, with a press washer, and also with a rubber gasket.

At the end of the installation of the roof covering, the end walls of the greenhouse are trimmed with polycarbonate, then the finished door is installed. It's great if it has a glazed part. In addition to all this, almost under the roof itself, the upper part of the ventilation, a kind of hole, is equipped, a pipe is attached there.
How to strengthen the building?
It is important to focus on the fact that you need to leave that part of the roof that faces the south side open to sunlight, because the sun stays there more time throughout the day. A different roof slope from the inside of the greenhouse is covered with foil insulation, which will reflect the light that enters it through the transparent part of the roof. For this purpose, it is optimal to use foamed polyethylene, the thickness of which is 5 mm, with a foil part.

Fastening occurs to the roof rafters thanks to self-tapping screws with a wide hat. At the junction, the insulation must be bent onto the wall. In a similar way, it is customary to insulate the walls of the greenhouse, the material is fixed on vertical stone planes with liquid nails, and even a crate of thin rails is arranged on the wall, plus polyethylene foam is fixed with self-tapping screws.

The tasks of the foil coating are considered not only to reflect light into the space, but also to save carbon dioxide, heat and moisture, which are vital in the course of photosynthesis that occurs in plants.
How to organize heating in a greenhouse?
To prevent heat from leaving the greenhouse or greenhouse for a long time, it is customary to install doors on the ventilation openings. The room can be heated in different ways, for example, the electrical system " warm house”, then convectors and a stove long burning. And if the greenhouse is located near the house, it’s really possible to carry out water heating directly from the gas boiler.
Suddenly, the “warm floor” system is installed, then before placing it, you need to prepare the bottom of the greenhouse, because the energy can go into the ground in vain. The system should be mounted under the beds, although, if necessary, it can be placed under the paths between them.

Preparation takes place in stages:
- a heat-insulating sheet is applied to the ground, it is good if foil is present in it;
- be sure to pour a layer of sand about 5 cm thick;
- a reinforcing mesh is applied on top, the cell size of which is 3x3 cm;
- then the heating cable is fixed;
- it is covered with a sand cushion of 5 cm;
- reinforcing mesh is laid again;
- 30-40 cm of soil is superimposed on it.
Each layer is laid in the formed beds, the sides are bricks or boards. The beds are usually arranged along the walls, but suddenly the greenhouse or greenhouse is wide, then an additional line is installed in the middle. It is good to create beds at a slight angle, so the surface of the soil will be slightly turned towards the transparent roof slope on the south side. Quite often, recently, convectors have been installed in the greenhouse for heating.

They really have a lot of advantages, which are ideal for greenhouses and greenhouses:
- minimally dry the air, in comparison with other heaters, because they are designed in such a way that they create an artificial circulation of warm air;
- easy to install, it is enough to hang the convector on a bracket mounted on the wall, plug it into the socket, and set the temperature level on the regulator;
- I am pleased with the presence of an automatic mode for turning the heater on and off, taking into account the selected temperature, this saves electricity;
- the device is small, with an aesthetic modern look.
Before you buy a convector for heating a large space, it is better to look at the characteristics of the device, take into account the power, then it will become clear how many heaters you need for your area. Another solution for heating is a long-burning cast-iron boiler with a water circuit.

To mount such a system, you have to work hard:
- first, it is the boiler that is installed, its installation is carried out directly in the greenhouse, or even in the next room;
- you need to carry out a chimney that can be raised to a height of at least 5 m;
- in order to pass the pipe through the hole equipped for it, it is better to isolate the combustible materials of the greenhouse from the high temperature during the heating of the boiler;
- it is important to calculate the correct slope of the pipes of the circuit, then carry out the supply, as well as the return pipes for the coolant, most importantly, correctly distributing the radiators;
- the system must be filled with water, then the temperature sensor must be installed directly in the greenhouse.
The installation of the described system, for sure, is really complicated, in comparison with other analogues, in particular, if we draw a parallel with the converter heating system.
When heating a greenhouse, it is important to note that for the normal development and growth of plants, it is necessary to maintain the air temperature at the level of +25…+30 degrees, while the soil temperature should reach +20…+25 degrees. Moreover, it is important to maintain a normal level of humidity in the room.
What will be the greenhouse or greenhouse on the foundation
A greenhouse mounted on a strip foundation will easily function throughout the year if it has the necessary conditions for this.

Accordingly, the assembly of the structure is carried out extremely carefully, because it must be generally airtight, not counting, of course, the installed ventilation system. For the frame, it is optimal to prefer wood, since it conducts cold minimally, in comparison with a metal profile, it is guaranteed to create “cold bridges”.

The frame for this version of the greenhouse is mounted in stages:
- on adobe or stone, plastered walls, which are 0.5-0.7 m above the ground, fit waterproofing material, basically, a classic roofing material;
- thick anchors are attached to it wooden bars, their width depends on the walls, and the height ranges from 5 to 15 cm;
- the gaps between the walls and the bars, and even the metal profile, it is better to close up with mounting foam;
- further work depends on what material will be the main one in the greenhouse, it may turn out to be a finished metal-plastic frame, or a justification for a metal or wooden frame;
- then double-glazed or triple-glazed windows are installed in metal-plastic frames, wood frames with glass or double-glazed windows are installed in a wooden frame, polycarbonate is usually attached to a metal counterpart.

The foundation, then the floor and the lower level of the greenhouse wall must be insulated. For this reason, in this case, it is better to prefer a "warm floor", its device is described above, and in addition it is necessary to install high-quality converter heating. It will maintain the temperature in the room.

If the greenhouse is located in a cold region where there is a lot of snow in winter, then when cleaning the yard from snowdrifts, it is better to pile the snow right next to the walls, it will serve as a heater, and will make it possible to save on heating in the winter. For walls, it is better to prefer thick glass, about 5-7 mm, or even cellular polycarbonate 10-15 mm. The honeycomb material has an air gap between the main planes, it all works like a heater.
Organization of lighting
Any greenhouse that is used in the winter should be additionally illuminated, so the spring state will appear in the room, due to the fact that the length of daylight hours, as well as the intensity of winter solar radiation, will be really small.

In order to save energy in the form lighting fixtures, it is possible to use lamps with LEDs. They are sometimes of different shapes, but are located only on the very high point ceiling. Naturally, if there is a desire, it is available to install classic lamps, they are mounted at the junction of the roof and walls, as an option - high directly on the walls.
To adjust the lighting hourly, it is possible to put a control unit with a specific timer, set the time on it when the light in the greenhouse needs to be turned on and off. The described system will make it possible to save energy, create extremely comfortable conditions for plants.
If a greenhouse or hotbed is needed only for the spring-summer period, it is not difficult to justify them, because no special warming conditions are required, but also lighting. Winter option, in turn, is extremely complex, especially in calculations and construction, and in everyday operation in general. Usually these complexes suit those people who professionally grow flowers and vegetables, some exotic plants. Thus, they simply cannot do without a comfortable room, with a special microclimate. All these maintenance costs will pay off over time when the sale of plants or fruits begins.














