How to distinguish a wild rose from a rose. Types of roses
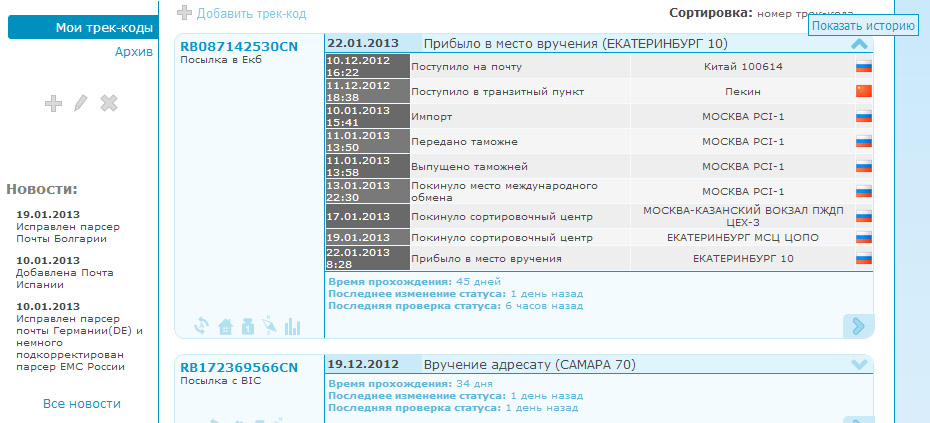
Everything is very simple - to track a registered letter of the Russian Post, it is enough to know its unique identifier (➤ where to find it, read here) ✅ Then you only need one action, a maximum of one and a half :) ➤ Enter the postal identifier of a registered letter in the tracking form and click on the image “magnifiers” - we will gladly and quickly do the rest for you. After a maximum of 10 seconds ⏳ our robot will track the letter and show all the information on the screen.
How much is a registered letter?
A very popular question - let's say right away, there is no exact answer to it. Delivery times for registered letters depend on many factors listed below:
- Distance between transportation points. The letter can be delivered within 24 hours after sending if we are talking about forwarding it within the same city. Forwarding a registered letter usually takes no more than 2 days within the cities-subjects of the Federation, or by the centers of administrations of the district district. If the destinations are located at large distances (from 1000 km or more), it is already more difficult to answer how long does a registered letter take?
- Weather. Delivery times for registered letters (as well as any other RPO) of the Russian Post are calculated based on average statistics that do not take into account possible deterioration in weather conditions. This is especially true in winter period because heavy snowfalls do not allow special mail transport to quickly overcome the route.
- Possible mistakes when filling out the form or when transferring data to the pochta.ru database. We are aware of cases where mistakes were made by the sender or the postal worker. Most often they are associated with an incorrectly filled in address or a postal code that does not match it. In such cases, a registered letter may be sent along the wrong route.
You can find out the approximate delivery time for a registered letter by calling the hotline of the Russian Post ➤ link to the page with a phone number. Or use the calculator for calculating the delivery time of letters on a special page of the Russian Post website: ➤https://www.pochta.ru/letters. To find out how much a registered letter takes, enter the initial and final destinations, then the estimated weight of the letter or the number of sheets in it, and the delivery method.
![]()
how long does it take for a letter pochta.ru
Tracking Russian Post letters by track number
✅ Our online service provides a service for tracking Russian Post letters by track number - it's completely free, and the tracking process is faster ✈ than most similar sites. ➤ To track a letter by number, you need to enter it in a special window and click on the “tracking” button - in our case, this function is performed by a “magic magnifying glass” :)
![]()
email tracking by number
How to track a letter of the Russian Post?
- As we all know, the process of tracking letters on the official (pochta.ru) is not the most convenient. And therefore, quite often, many customers of the Russian Post have a question - how to track a letter? We disinterestedly :) will be happy to answer this question and help you track your letter. Email tracking is impossible without 2 components:
- This is the track number assigned to the letter at the Russian Post office. If on this stage the question arose in my head - what is it? ➤ read the answer here.
- Good quality online email tracking service - don't worry, you've already found it :)
Drive the number into the window for tracking letters and click on the image of the “magnifying glass” - you see, tracking the letter is not as difficult as it seemed;)
How to track a regular or registered letter by last name?
✅ It is not uncommon for site users to be interested in the possibility of tracking letters by last name. ➤ The good news is that we know everything existing ways track the letter, but there is also unpleasant news - unfortunately, by last name, do it on this moment impossible. If any of the Internet resources offers you tracking by last name, we do not recommend doing this. As you probably know, “demand creates supply” and sometimes not as good people as we are trying to make money on this :) people. Under the pretext of tracking the letter, you will be asked to enter your last name, and then most likely send an SMS and believe it will not be free;). As a result, you will not receive the promised information on the letter, thanks for your attention - be careful and good luck;)
What is a mail ID and where can I find it?
➤ So, let's try to quickly bring you up to date and tell in a couple of sentences what a track number is - it's also a postal identifier. Oddly enough, but none of these designations are used by the Russian Post in the check, which is kindly provided to you at the office. ✅ RPO - this is the official designation of this miracle number :) “RPO” stands for registered mail and it is this identifier that makes it possible to track your letter among thousands of others. As we already hinted above - you can find the tracking number of the letter in the cash receipt, especially for you we took a photo of the check of the Russian Post and marked the location of the track number with a hefty red arrow, good luck in your search;)
![]()
pochta ru track a letter by number
How to fill out an envelope?
- It would seem a common thing to fill out an envelope to send a letter, but it is important to do it correctly so that the letter is delivered as quickly as possible and to the right address. Not everything is so complicated, following our instructions you will become an expert :) in filling out envelopes, point by point:
- It is necessary to indicate the addresses of the sender / recipient and their full name as legibly as possible
- AT right bottom corner contact details required sender
- Fill in the upper left corner with the Recipient's data
- Filling the envelope - what to indicate in contacts:
- Full “Surname First Name Patronymic” of the recipient and sender. If the recipient / sender is an organization, you can indicate its short name.
- Rooms: streets, houses and apartments (in case it is an apartment building, and not a private house)
- Full name of the settlements of the sender and recipient of the envelope
- Name of the district, region, territory or republic
- If the envelope is sent to another country, you must specify its full name
- P.O. box number - if the envelope needs to be delivered to a different address than the recipient.
- Postal codes of the recipient and sender - fill in carefully, due to an error in one digit, the envelope may “leave” in the wrong place.
Below is an example of the correct filling of the envelope:
![]()
how to sign an envelope
Thank you very much for choosing our service - we appreciate it and are constantly working to improve the entire process of tracking Russian Post letters.
When making purchases in foreign online stores, we all somehow face the issue of tracking the postal item that delivers the purchased goods to us.
This article will consider general issues regarding the tracking of international mail (IGO). Will be considered general principles according to which IGOs are divided into traceable and non-trackable, the main stages of delivery that shipments go through. The issue of the structure of international tracking numbers assigned by IGOs is considered separately.
We will also talk about average delivery times and factors that greatly affect these times. A separate section will provide information on the possibilities of tracking IGOs on the websites of the state postal services of the countries of the sender and recipient, as well as the use of universal independent services for tracking.
another Additional information on these issues, as well as on the issues of customs clearance of international mail and the work of individual postal services, you can always find in the wiki section of this site.
Basic principles Traceable and non-traceable IGOs
Traceable and non-traceable IGOs
IGOs (international mail) are divided into two main categories:
- Parcels(over 2 kg)
- small packages(up to 2 kg)
MPOs are also divided into:
- Registered(with traceability)
- Unregistered(without traceability)
Parcels, as well as any shipments via EMS, are always registered shipments, but small packages can be either registered or unregistered.
A registered IGO in the country of departure is assigned a unique 13-digit tracking number, which can be used to control the movement of IGOs from the sender to the recipient, using the tracking services of the national postal operators of these countries or independent tracking services.
The tracking number for registered small packages always starts with a letter R(Registered).
Accordingly, tracking the movement of IGOs using tracking services is possible only for EMS shipments, parcels and registered small packages, provided that you know the tracking number.
Examples of tracking numbers:
- CQ123456785US - mail from the USA (package)
- RN123456785US - mail from the USA (small package)
- EE123456785US - US EMS
- RA123456785CN - mail from China
- RJ123456785GB - mail from the UK
The last 2 letters in the tracking number indicate the country in which the shipment is accepted for shipment. You can read more about the structure of the track number in the next section.
When an unregistered MPO arrives in Russia, the Russian Post assigns it an internal tracking number of the RA*********RU type. This number is the internal information of the postal operator and serves for internal accounting of incoming international mail and subsequent settlements with the postal operator of the country of departure.
The recipient can find out this number only upon receipt of the IGO.
Track number structure
According to the rules of the UPU (Universal Postal Union) (standard S10), the IGO track number consists of 9 digits and 4 letters. Track number structure: XX***********XX, where X are letters and * are numbers.
Example: RA123456785GB
The first two capital Latin letters indicate the type of postal item. Here are the main ones:
- LA-LZ- unregistered IGO weighing less than 2 kg (small package). Not tracked.
- RA-RZ- registered IGO weighing less than 2 kg (small package). Tracked.
- CA-CZ- registered MGO weighing more than 2 kg (package). Tracked.
- EA-EZ- registered IGO, issued as express mail (EMS). Tracked.
Further, the track number indicates an eight-digit digital unique MPO number. According to UPU rules, it cannot be repeated for at least one year. The last (ninth) digit is a verification code calculated using a certain mathematical function from the departure number.
At the end of the track number, two capital Latin letters are also indicated, which abbreviated the sender's country according to the ISO 3166-1-alpha-2 code standard. For example CN- China, SG- Singapore, GB- Great Britain, DE- Germany, US- USA, etc.

2. greatly simplifies the procedure for tracking registered mail using the track number provided by the user and combines the tracking systems of postal services from 27 countries of the world. Allows you to create lists of checked track numbers, keeps statistics on the average delivery time of items from different countries. Allows you to predict the time of passage of the departure of one or another stage of delivery.
3. - can be installed both on a PC and on personal mobile devices. The list of supported services is more than 250 mail services. Allows you to create lists of checked track numbers. In addition, it is possible to add user data to the tracking number, which allows you to have accurate information about all the events that occur with a specific order from the moment it is paid in the store until it is delivered to the addressee.
In addition to the above, there are many other mail tracking services with different capabilities and different composition of supported mail services, so it makes little sense to list them. It stands a little apart, perhaps, which tracks China Post parcels well, but has a rather inconvenient interface and does not support many recently emerging local Chinese logistics companies.
Why tracking for a regular buyer
In this final section, I would like to say a little not only about the technical side of the issue, which the article was devoted to, but also about the psychological side of the tracking issue. And also talk about the general goals of tracking.
It is quite understandable that all buyers want to receive their goods as quickly as possible and secretly hope that the goods sent from, say, China or the USA will reach the recipient in Russia in a week. But, alas, miracles do not happen and when choosing the delivery of goods by the usual state postal service, you need to be mentally prepared to wait 3-4 weeks.
During this time, someone will check their track number just a few times to make sure that the shipment is moving, and someone will check their track number several tens or hundreds of times ... Of course, the latter is more common for online shopping beginners and their excitement even somewhere justified. But the truth lies in the fact that no matter how many times we check our track number, the package will not move faster from this! Therefore, you still should not be so paranoid about tracking issues.
In fact, tracking is a tool for controlling the physical movement of a shipment, in principle, a tool for monitoring compliance with delivery times. And the tracking data of the shipment, for example, will be very useful to you if you decide to make any claims to the postal services regarding the delivery of the shipment or the speed of delivery.
Therefore, three main purposes of tracking can be identified:
- Informational - when the recipient simply monitors the movement process and the delivery time of his shipment, receiving information from tracking systems.
- Control - when the recipient, with the help of information from tracking systems, can control the timing of the shipment at certain stages of its processing and delivery in order to correlate these deadlines with the target delivery deadlines and receive any compensation from the postal services, in case of non-compliance with these deadlines.
- Evidential - when information from tracking systems serves as evidence in possible disputes between the sender and the recipient, in case of non-receipt of the shipment or its loss (alas, this also happens sometimes)
To reduce the time for the tracking process itself, of course, it is recommended to use independent tracking services that allow you to create lists of tracked track numbers. The track number is added there once and only then you can safely watch the tracking results every 1-2 days. This greatly reduces the tracking time for all your parcels and saves your nerves.
Good luck with your shopping and fast shipping!
- Rosehip: types and varieties
- How to determine the freshness of roses
- What roses are called tea
How to distinguish by the type of leaves




During flowering
In fact, rose flower

By escape






- one family;


Leaves

shoots

When growing roses, remember that improper care can provoke the degeneration of bushes in the direction of an ordinary wild rose.
Video "How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose"
From this video you will learn how to quickly distinguish a rose from a wild rose.
%0A
%0A %D0%9F%D0%BE%D1%85%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%B8%D0%B5%20%D0%B7%D0%B0%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%81 %D0%B8:
10 sen
How to identify a rose or wild rose
- How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose by leaves and shoots
- Rosehip: types and varieties
- How to determine the freshness of roses
- What roses are called tea
Of course, when buying a seedling, it should be carefully examined. Experienced gardeners can distinguish the "queen of flowers" from the usual wild rose at a glance. To do this is actually extremely simple.
How to distinguish by the type of leaves
First of all, when buying a seedling, the gardener should take a closer look at the leaves of the plant. Both the wild rose and the rose have quite spectacular and have an unusual structure. In both of these cultures, each leaf consists of a "twig" and several small leaves growing on it. Asking the question of how to distinguish a rose from a wild rose, the first step is to count the number of the latter. Rose hips have 7 leaves on each "twig". In a rose, their number never exceeds 5. Sometimes on the "branches" of this culture, 3 leaves grow. Also, in rose hips, the topmost leaf is usually unpaired.

The leaves of the rose have a very dark glossy color and are quite large. In rose hips, they are small, more delicate and matte. Also, the leaves of this plant have a pale green light color.
How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose by the type of shoots
On this basis, distinguishing plants is also not difficult. The rose shoots have a reddish color. Over time, they become woody and acquire a dark green color. The wild rose shoots are more tender. In addition, they initially have a light green color. If nothing red is noticeable on the seedling, it is most likely a wild rose.
Also, when buying a rose for planting, you should pay attention to the thorns of the bush. In roses, they are usually very long and rarely located. In rose hips, the spines are short and often distributed. Sometimes they even appear on the leaves and sepals of this plant.
The main distinguishing feature of a rose is its red shoots. The thorns of some varieties are also short, and the leaves are seven-petal. It is on the color of the shoot that you should first of all pay attention.

What to do if the rose turned into a dog rose
So, we figured out how to distinguish a rose from a wild rose by leaves and shoots when buying a seedling. But sometimes summer residents have problems with the "queen of flowers" even if she has already taken root on the site. The plant is tender and can easily freeze in winter. Often after this it happens that the shoots begin to grow "from the root." In this case, most often the rose turns into a wild rose. If the shoots go above the grafting site under the ground, the owners of the garden will again receive the "queen of flowers". Below the grafting site, only rosehip shoots sprout.
What to do if the rose has turned into a wild rose? In order to remedy the situation, garden owners just need to take a closer look at the bush. It often happens that along its edges a lot of wild rose shoots grow. In the middle, you can see a couple of rose branches. All that needs to be done in this case is simply to remove the rosehip.
It should be done correctly. If the rose has turned into a wild rose, it is worth cutting off unnecessary shoots by digging up the flower beds a little. Weed shoots are removed in this case right underground - at the very base. Otherwise, in the future, the rose will not look too neat, and the wild rose will begin to sprout again.
Sometimes rebirth also occurs due to improper selection of a stock or violation of planting technology. In this case, the rosehip shoots simply clog the rose shoots. It is necessary to plant the "queen of flowers" with a slight deepening of the grafting site.

Now you know how to distinguish a rose from a wild rose. Prune the first to prevent rebirth, usually twice a season. This method is, therefore, rather troublesome. It is much easier to immediately transfer the rose to “its roots”. Carry out this procedure in the spring, after thawing the soil. At the same time, a trench is dug from the trunk of the bush. Then they bend and fix one of the shoots in it. Subsequently, the branch will give roots and a new separate rose bush will appear in the garden.
You can use this method only for winter-hardy varieties of the "Queen of Flowers". A bush grown in this way will reach full decorativeness for 4-5 years.
 Many, especially inexperienced gardeners, complain that an ornamental rose bush turns into a wild rose bush in a year or two. This situation can be avoided if you know the differences between rose and wild rose.
Many, especially inexperienced gardeners, complain that an ornamental rose bush turns into a wild rose bush in a year or two. This situation can be avoided if you know the differences between rose and wild rose.
During flowering
In fact, rose flower and is a wild rose, only cultivated. It's pretty easy to tell them apart. There are, of course, exceptions, but for beginner gardeners they are rather informative. During the flowering period, it is very easy to distinguish an ornamental plant from a wild one.
The first in a flower, as a rule, has a lot of petals, and the second has only five. Also, when looking at a rose, it is rare to see its middle. There are varieties where it is open on purpose, but they still have a lot of petals. Rose hips have a yellow center always in sight. Rose bush flowers have a huge number of shades of flowers - from white to almost black. Rosehip flowers are only white, pink or bright pink. But there are examples of the opposite. 
And such differences are known only to experienced gardeners. To distinguish a wild plant from a noble one, it is enough to look at the differences in the complex.
By escape
The queen of flowers from the wild rose is very easy to distinguish by shoots. In a noble plant, they are red-burgundy in color, which can later turn green. And in a wild representative of the family at a young and mature age, they are always invariably green. Experienced lovers of the queen of flowers say that some scrubs and climbing representatives of the pink species also have green shoots. Then you need to look at the flower and the leaf.  A rose can be distinguished from a wild rose both by shoots and leaves. The leaves of both representatives of the Rosaceae family are different, as are their different numbers on a complex leaf. Rose hips always have seven leaves on a branch.
A rose can be distinguished from a wild rose both by shoots and leaves. The leaves of both representatives of the Rosaceae family are different, as are their different numbers on a complex leaf. Rose hips always have seven leaves on a branch. 
A rose should normally have from three to five. But even here there are exceptions to the rule. In new varieties of ornamental crops, the number of leaves of more than five indicates their good winter hardiness, so there may be varieties that have seven or more leaves in a complex leaf. Also, more than five leaves occur in climbing varieties.
Therefore, further, in order to figure it out, you need to see what kind of leaves the rose has. They are larger in size and rich green in color, dark, sometimes even with a burgundy tint, as if glossy. And in the wild representative of the species, they are small, sometimes with small spikes, in color they are bright green and more matte than glossy.  The two plants also differ in thorns. In the rose bush they are large, rare, and in the wild rose they are small and frequent.
The two plants also differ in thorns. In the rose bush they are large, rare, and in the wild rose they are small and frequent.
Correct rosehip pruning (how not to turn a rose into a rosehip)
The differences are clear, but why do roses turn into wild roses, how to avoid this, and what to do? To answer these questions, let's figure out how a decorative representative of the species gets into our garden. The plant can be with its own root system, or it can be grafted onto the so-called "rootstock". The latter case is more common, because with such a grafting, rose bushes are more resistant to soils, pests, and changing climatic conditions. And all because the stock is a wild representative of the species. That is, very often a pink seedling has a root and a basal part from a wild rose and only an upper shoot from a decorative rose. If you take a closer look at the seedling, then at the bottom it has a thickening, from which shoots extend. In the place of thickening, cuttings of a cultivated species are grafted onto a wild plant. A rose with its root system does not have this.  If suddenly you notice that shoots grow from the root of a rose bush that have a bright green color, you need to get rid of them. These are the shoots of the wild parent, which are usually below the graft. They must not only be cut at ground level, but removed from the root system. To do this, you need to carefully dig the ground around the plant and remove everything that is below the grafting site. As a rule, this will be the growth of wild rose. Anything above the inoculation should not be touched. These are new rose shoots.
If suddenly you notice that shoots grow from the root of a rose bush that have a bright green color, you need to get rid of them. These are the shoots of the wild parent, which are usually below the graft. They must not only be cut at ground level, but removed from the root system. To do this, you need to carefully dig the ground around the plant and remove everything that is below the grafting site. As a rule, this will be the growth of wild rose. Anything above the inoculation should not be touched. These are new rose shoots.
There are times when you can see wild shoots a meter from a rose bush. They also need to be removed. They take strength from the main plant, it grows and blooms worse.
The rose has turned into a wild rose: what to do
The rose completely transforms into a wild parent if the graft is dead. This is the part of the plant that is above the graft. In this case, shoots begin to grow actively from the rosehip buds. This is especially true for young plants that do not tolerate winter well. If this happens, you can transplant the bush outside the site.
There are cases when the decorative part did not die completely, that is, its processes still remained in the bush. You can try to save the plant. All rosehip shoots are pruned, and annuals are used as rootstock for roses. On their bark, you need to make an incision, place a kidney from a rose there and wrap it up. After a couple of weeks, the bud will take root, and next year a noble shoot will grow out of it. Usually such a procedure is done at the end of summer and it makes it possible to save an ornamental plant.
Experienced gardeners say that in most cases, an ornamental plant is reborn into a wild one due to inept care. If you follow all the recommendations described above, this can be avoided. With proper care, beautiful decorative rose bushes will not upset you, but will delight you with beauty and aroma for a long time. 
Differences between plants of the rose family
The rose, like its close relative, belongs to the Rosaceae family. This fact explains why these two different plants are difficult to distinguish from each other, especially at the seedling stage.

Rose is a member of the genus Rosehip. Therefore, it is very often grafted onto this bush. It was obtained through painstaking selection work of scientists from around the world. To date, this flower is represented by a variety of varieties, the flowers of which have both a different color of the petals and the structure of the inflorescences. To obtain such a huge variety, the method of multiple crossing was used. At the same time, some species are forms of wild rose hips. Therefore, both plants have a genetic and external similarity.
At the same time, it should be understood that a rose is a collective name that contains various representatives of this genus. Therefore, it is not surprising that novice flower growers often confuse these plants. General points here include:
- one family;
- some varieties of roses are considered a cultivated wild plant.
However, despite certain similarities, both plants have obvious differences. For example, rosehip, despite the external similarity, is different in that after flowering it forms a fruit that is very rich in vitamin C. According to this indicator, it even surpasses citrus fruits.

The main distinguishing characteristic of both cultures from other plants is the characteristic structure of the flower. It is bisexual and has a double perianth. The flower calyx has five fused sepals. The flowers themselves can be collected in inflorescences or located separately.
To distinguish a rose from its close relative, you need to know what to look for when buying a seedling for growing in the garden.
The main differences between rose and wild rose
The most common mistake novice flower growers who are going to breed roses is buying seedlings of a different kind. The main differences between these two closely related plants is the fact that they form different flowers. The differences here lie in the following:
- the rose has more decorative and beautiful flowers. Its flowers are characterized by a larger number of petals. Rosehip has five petals as standard;
- the fruit-forming relative blooms in small flowers, which may have a slight doubleness. However, in these parameters they are significantly inferior to the rose. Its flowers have a pronounced core;
- after flowering, rose hips form oval/round fruits. The fruits contain seeds inside. Wild varieties produce red fruits, while cultivated varieties are blue-black or orange. But roses (any variety) do not form fruits at all. After flowering, the petals from the bushes simply crumble;
- plants differ in the color of the petals. Rose hips are characterized by a light pink color. But roses can bloom in inflorescences of various colors: white, red, orange, pink, etc.

However, when buying seedlings, it is still impossible to evaluate plants by flower parameters. Therefore, here it is necessary to be guided by other parameters of the assessment. First, you should ask the seller if the bush has been grafted. Grafted plants have a slight thickening at the bottom of their shoot, which is the place of grafting. Below the thickening, the stem may acquire a different color.
It should be noted that own-rooted varieties of roses are not grafted. In this case, you need to rely on other parameters in which the rose differs.
In addition to the above points, a rose and a wild rose differ in leaves, shoots and thorns. Let us consider these parameters in more detail, since it is on them that attention is always focused when choosing a seedling.
Leaves
You can tell one plant from another by its leaves. In roses, the leaf blade has a dark green color. At the same time, it has slightly rounded tips, leatheriness and density, as well as a shiny surface. Its leaves are larger. A rose has 3–5 leaves on a leaf branch, and a relative has 7 leaves.

Rosehip leaves are rough and dull. They usually have a light olive color. The leaf plate has a pointed tip. Edges may be uneven. Sometimes the leaves are characterized by pubescence and thorns.
shoots
The rose has young shoots of dark red color. Over time, they turn green and woody. But the shoots of the analogue are always bright green. They also form thinner.
Already on the basis of the differences between the leaves and shoots, you can determine which particular seedling they are trying to sell you.

Those who are not completely convinced by the leaves and stems should rely on such a parameter as thorns when choosing a seedling. Roses are characterized by rare, but rather large thorns. Therefore, they are considered more traumatic, although similar formations in a relative are no less dangerous. At the same time, wild rose shoots are completely strewn with short and small thorns. Here, thorns can be found not only on the stems, but also on the sepals and petioles. It is because of the abundance of spines that this plant got its name.
Despite the presence of such obvious differences, the rose still manages to pass itself off as a wild rose and vice versa. Such confusion is connected with the fact that the distinctive characteristics of these plants can be smoothed out to a certain extent by multifaceted selection work. And only a true professional can distinguish one culture from another.
Categories: / / from 10.09.2019Rose and wild rose belong to the same family - Rosaceae and have much in common. Their species are very closely intertwined, and some types of wild roses are considered wild roses and vice versa. But still, these plants are different from each other.
- Exploring the differences
- More about rose hips
- A little about roses
Exploring the differences
During the flowering of plants, answer the question: "How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose?" worth nothing, the difference is obvious. Just look at the flowers: roses have many petals, while rose hips have only five. In addition, the wild rose bears fruit, which cannot be said about the rose. Therefore, at the end of summer, the difference between a rose and a wild rose is obvious, the last plant is distinguished by red or orange bright berries.
But if, when planting, it becomes necessary to distinguish between the shoots of roses and wild roses? Let's name a few signs by which it becomes clear how to distinguish a rose from a wild rose by shoots.
4 differences between rose and wild rose shoots
- The rose produces red shoots, which then turn green, in the wild rose, the young shoots are immediately green.
- The rose has 3 - 5 leaves on a branch, the rosehip has 7 of them, the top one does not have a pair.
- The color of the leaves of the rose is dark green, the leaves are hard, large and glossy, the wild rose has small, light green, matte leaves.
- Thorns of roses are rare and large, rose hips are frequent and small. Sometimes the sepals and even rosehip leaves are covered with thorns.
If cultivated roses are grafted onto wild roses, then savage shoots often climb from the roots. This situation is unpleasant in that the dog rose draws all the food onto itself and weakens the culture. After all, its growth capacity is an order of magnitude higher. In this case, a layer of soil under the bush is raked to the depth of shoot growth, and the rosehip is cut flush with the root. Otherwise, on the cut, it will begin to branch, instead of one, it will release many shoots.
More about rose hips
In temperate and cold zones, wild roses, which we call wild roses, usually bloom for a short time - in May-June. And subtropical evergreen savages bloom almost continuously. Our species give fruits in August-September. They are very meaty and juicy. Inside the rose hips are bristly villi, which, as it were, wrap up hard nut fruits.

Rosehips in free growth grow most often in large bushes, up to 2 m tall. Branches erect, slightly drooping. There are creeping species, the branches of which can cling to the trunks of trees and neighboring plants. So their shoots rise high enough.
There are bushes in the form of pillows, then the growth of their bushes is low, dense. During flowering they are very decorative. The flowers are distinguished by numerous stamens and pistils, the petals can be white, yellow, pink, red and crimson.
Cultivated wild roses are called park roses in international botanical terminology. They are actively used in landscaping, they have a very successful landscape, close to nature, appearance. One of the elegant wild roses is a wrinkled rose, or rugosa rose (Rosa rugosa), and hybrids created on its basis (Hybrid Rugosa).
It is recognizable by its wrinkled leaves and styloid dense straight bristles and spines along the shoots. Her smell is pleasant, fragrant, but weakly expressed. The flowers are non-double, flowering continues all summer. Bushes are very durable and unpretentious. They do well in borders and hedges, and can also be planted singly or in groups. The main advantage for our latitudes is frost resistance in winter. In winter, they can be left without any shelters.
A little about roses
Watching roses, which are universally popular, one may not notice that in recent years a lot has changed, and the accumulated changes are already beginning to actively put in order, classify. Separated into special groups are patio roses, ground covers. Climbing miniatures appeared, which have unusual small flowers and crumble leaves.

Many articles have been written about new varieties, we will talk a little about flower shapes. According to the shape of the flowers, roses are divided into 9 main types:
- With a cone-shaped center - classically shaped buds, characteristic of hybrid tea varieties, in which the petals are folded into a cone.
- Peony, or spherical shape - numerous petals are concave inward, cover the center of the flower.
- Form with a loose center - loosely closed petals form a core of indefinite outlines.
- Collapsing form - at the end of flowering, the flower of the initially correct shape loosens, the petals seem to fall out, exposing the stamens.
- Cupped shape - numerous rose petals form a cup, the center of the flower is not covered.
- Square shape - the inner petals create, as it were, four sectors located radially outward of the flower.
- Pompom shape - numerous short petals form a rounded, almost spherical outline of the flower.
- Flat form - a flower with numerous petals, slightly concave towards the middle of the flower.
- Rosette-shaped - the whole flower seems to flow down to the middle, concavity is noted, but its shape itself is flat with numerous short petals.
Studying the differences between wild rose and rose, four main differences in shoots were identified. A brief description of wild roses is given, their decorative qualities for the garden are given. In the description of varietal roses, their modern classification is given according to differences in the shape of flowers. Roses and wild roses are very interesting crops for home gardening, it is always a pleasure to watch them grow and bloom.
gardensadovod.com
Rose and wild rose
Growing garden roses by budding is much easier than getting from cuttings. Rose hips (wild rose) are used for stocking roses, which is found everywhere - from Central Russia to the Far East.
- unpretentious;
- frost-resistant;
- undemanding to soils;
- easily accepts grafted vegetative material.
Roses grafted onto wild rose survive in 80% of cases on the powerful roots of the plant, grow and bloom profusely the next year. Rosehip is used for budding of all types of roses - ground cover, climbing, floribunda, park.
The park rose is a cultivated rosehip hybrid, undemanding to care and hibernating without shelter. In terms of abundance of flowering and variety of shades, it is not inferior to hybrid tea roses. A vigorous bush and small-double flowers of park roses are often confused with a wild rose (rose hip).
elenamumrina
http://www.rfc-online.ru/?page=109&group_id=20&event=notes¬e_id=1575
Similarities and differences
According to the classification botanical features, rose and wild rose belong to the same genus Rosa and the Rosan family. They are very similar: both shrubs are thorny, have a similar shape of leaves, bloom with fragrant beautiful flowers - corymbs from May to the last decade of August. By a number of features, these plants can easily be distinguished.
Table: differences between rose hips and garden roses according to botanical characteristics
Invincible Briar
After 3–4 years, strong shoots of the wild stock, resistant to diseases and temperature extremes, begin to germinate, clogging the cultivated scion.
A delicate capricious rose can completely wither and stop blooming. In one season, a powerful wild rose can irreversibly destroy the vaccine.
Despite the large inflorescences, the abundant growth of shoots, with improper budding, the wild rose “won” my floribunda the very next year. And on groundcovers with climbing stems and small semi-double flowers, wild rose is especially noticeable. Rosehip does not bloom on vaccinations, that is, from a crazy-smelling splendor, a rose turns into a prickly, nondescript, completely impregnable outcast bush.
Why does a rose turn into a wild rose
A conscientious and competent approach to grafting a cultivated rose is a guarantee of high-quality budding and longevity of a new variety on wild rose hips. When propagating, the place of budding (thickening with shoots) of the grafted rose is buried at least 3–5 cm below ground level, this will strengthen the scion cutting and increase its survival rate.
The lower part of the bush is spudded annually, because due to precipitation and wind, the soil sags over time, the graft is exposed.
It must be remembered that if weak, diseased cuttings are selected for budding, the graft will not be able to take root on the wild rose, which, at the first opportunity, will give “wild” shoots and destroy the graft.
Video: why a rose turns into a wild rose
How to deal with it
On the 3-4th year, the first growth of the rootstock may appear, so you should carefully study all the young shoots. If the first sprouts of a “wild” rose appear, drastic measures must be taken immediately.
- The place of germination of the wild rose is determined (roots with "wild shoots" can grow up to 50–70 cm from the mother bush) and completely dug out.
- The shoots are cut with a pruner or a sharp knife under the base of the root (without leaving a single bud).
- The cut site is treated with iodine or garden pitch.
Re-sprouting wild rose is immediately removed again. This can be repeated 2-3 times per season. Proper care and observance of agricultural technology will not allow the game to displace the "cultural" vaccination. High-quality seedlings develop quickly and rarely give the rose hips an opportunity to express themselves.
Budding is a common way to propagate roses, because grafting roses is much more efficient and cheaper. In order not to deny yourself such pleasure and to receive pink abundance in your own flower bed every year, you need to be patient and not be lazy. If you regularly deal with wild game growth and follow the agricultural practices of cultivated roses, the flower garden will delight with aroma and amaze with beauty from late spring to late autumn.
orchardo.ru
During flowering
In fact, it is a wild rose, only cultivated. It's pretty easy to tell them apart. There are, of course, exceptions, but for beginner gardeners they are rather informative. During the flowering period, it is very easy to distinguish an ornamental plant from a wild one.
The first in a flower, as a rule, has a lot of petals, and the second has only five. Also, when looking at a rose, it is rare to see its middle. There are varieties where it is open on purpose, but they still have a lot of petals. Rose hips have a yellow center always in sight. Rose bush flowers have a huge number of shades of flowers - from white to almost black. Rosehip flowers are only white, pink or bright pink. But there are examples of the opposite. 
 For example, the ornamental variety "Mermaid" has only five petals, like a wild plant, and the wrinkled wild rose has up to 182 petals in a flower, like a rose. These cases, like the varieties mentioned, are rare.
For example, the ornamental variety "Mermaid" has only five petals, like a wild plant, and the wrinkled wild rose has up to 182 petals in a flower, like a rose. These cases, like the varieties mentioned, are rare.
And such differences are known only to experienced gardeners. To distinguish a wild plant from a noble one, it is enough to look at the differences in the complex.
By escape
The queen of flowers from the wild rose is very easy to distinguish by shoots. In a noble plant, they are red-burgundy in color, which can later turn green. And in a wild representative of the family at a young and mature age, they are always invariably green. Experienced lovers of the queen of flowers say that some scrubs and climbing representatives of the pink species also have green shoots. Then you need to look at the flower and the leaf.  A rose can be distinguished from a wild rose both by shoots and leaves. The leaves of both representatives of the Rosaceae family are different, as are their different numbers on a complex leaf. Rose hips always have seven leaves on a branch.
A rose can be distinguished from a wild rose both by shoots and leaves. The leaves of both representatives of the Rosaceae family are different, as are their different numbers on a complex leaf. Rose hips always have seven leaves on a branch. 
A rose should normally have from three to five. But even here there are exceptions to the rule. In new varieties of ornamental crops, the number of leaves of more than five indicates their good winter hardiness, so there may be varieties that have seven or more leaves in a complex leaf. Also, more than five leaves occur in climbing varieties.
Therefore, further, in order to figure it out, you need to see what kind of leaves the rose has. They are larger in size and rich green in color, dark, sometimes even with a burgundy tint, as if glossy. And in the wild representative of the species, they are small, sometimes with small spikes, in color they are bright green and more matte than glossy.  The two plants also differ in thorns. In the rose bush they are large, rare, and in the wild rose they are small and frequent.
The two plants also differ in thorns. In the rose bush they are large, rare, and in the wild rose they are small and frequent.
Correct rosehip pruning (how not to turn a rose into a rosehip)
The differences are clear, but why do roses turn into wild roses, how to avoid this, and what to do? To answer these questions, let's figure out how a decorative representative of the species gets into our garden. The plant can be with its own root system, or it can be grafted onto the so-called "rootstock". The latter case is more common, because with such a grafting, rose bushes are more resistant to soils, pests, and changing climatic conditions. And all because the stock is a wild representative of the species. That is, very often a pink seedling has a root and a basal part from a wild rose and only an upper shoot from a decorative rose. If you take a closer look at the seedling, then at the bottom it has a thickening, from which shoots extend. In the place of thickening, cuttings of a cultivated species are grafted onto a wild plant. A rose with its root system does not have this.  If suddenly you notice that shoots grow from the root of a rose bush that have a bright green color, you need to get rid of them. These are the shoots of the wild parent, which are usually below the graft. They must not only be cut at ground level, but removed from the root system. To do this, you need to carefully dig the ground around the plant and remove everything that is below the grafting site. As a rule, this will be the growth of wild rose. Anything above the inoculation should not be touched. These are new rose shoots.
If suddenly you notice that shoots grow from the root of a rose bush that have a bright green color, you need to get rid of them. These are the shoots of the wild parent, which are usually below the graft. They must not only be cut at ground level, but removed from the root system. To do this, you need to carefully dig the ground around the plant and remove everything that is below the grafting site. As a rule, this will be the growth of wild rose. Anything above the inoculation should not be touched. These are new rose shoots.
There are times when you can see wild shoots a meter from a rose bush. They also need to be removed. They take strength from the main plant, it grows and blooms worse.
agronomy.com
Which rose has 7 leaves
First, remember what kind of rose you purchased. It's no secret that many floribunda ( Carte Blanche, Red Leonardo da Vinci), climbing ( Polka, Super Dorothy, Flammentanz, Rosarium Uetersen), ground cover ( Lipstick) and scrubs ( Caramella, Maiden's Blush) a leaf can consist of five, seven or even nine leaflets.
If you are purchasing seedlings from a nursery, do not hesitate to ask the seller what to expect and what is normal for roses of this species. If the bush was bought in a shopping center or via the Internet, study the characteristics of the variety - look for information about it on rose websites or read special literature.
More than you are used to seeing, the number of leaves indicates, first of all, that the memory of wild ancestors is strong in the pedigree of your rose. Even the most beautiful and cultivated among roses can periodically throw out a few atypical leaves without losing their decorative effect.
How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose
Since Soviet times, it has been customary to distinguish a rose from a wild rose just by the number of leaves. This is due to the fact that the few varieties available at that time were classified as cut and were supplied from the Baltic states. All of them had five leaves, were capricious and did not tolerate winter well. But the wild rose, on the contrary, was not afraid of cold weather and actively grew in the most severe conditions. Now that roses can have any number of leaves from 3 to 9, other signs are worth paying attention to:
- The shoots of roses are at first reddish in color and only then gradually turn green; wild rose shoots are immediately green.
- Rose thorns are large and rare; the thorns on the branches of wild rose are small, densely spaced, grow not only on the stems, but also on the leaves, and next to the inflorescences.
- Rose leaves are bright, glossy, dense in structure, with a sharp tip; wild rose leaves are small, soft, matte, rough to the touch, with a rounded tip.
- New shoots of roses begin to grow above the grafting site; rosehip branches come from the root, from under the ground.
What to do if a rose degenerates into a wild rose
You can often hear that a cultivated rose suddenly degenerated into a wild rose, lost all the signs of a variety, and then stopped blooming altogether. Let's see how and why this happens.
If your rose is grafted, then there is always a chance of running wild. This can happen because the wild rose is a very strong plant, and its rootstock is very viable. But cultivated varietal roses, on the contrary, are weak and sensitive to the slightest changes in conditions for the worse. A strong rosehip root is able to give its own growth, which will quickly displace the vaccine, take away all its strength, and the rose will degenerate.
It is quite simple to understand that the development of a plant has gone in an undesirable way for you, if you regularly pay attention to your roses. A green shoot with small leaves and many thorns that appeared from the ground nearby (and sometimes at a distance of up to 2 m) indicates that the wild rose has declared war on you. Such branches grow very quickly and take all the strength from the rose. For a couple of months, next to a small floribunda, several one and a half meter branches as thick as a finger can grow.
If you notice that rose hips have appeared next to the rose, you need to take urgent measures - it will not go away by itself.
- Rake the ground near the root of the rose so that there is a place where the growth comes from.
- Break out all the wild offshoots, like stepchildren on tomatoes. If they are already very thick and do not break off, use a pruner, but cut exactly at the root, slightly deepening.
- Treat the fracture sites with crushed coal, a saturated solution of potassium permanganate or iodine.
- Fill the trunk with earth, compact it.
- After 3-4 days, give the rose a foliar top dressing with superphosphate (dissolve 50 g in 1 liter of hot water, then dilute the composition in 10 liters of water).
- Repeat the procedure until the wild rose has used up all the dormant buds.
Do not cut the shoots above the ground, from this it will begin to bush even more magnificently and draw even more strength from the rose.
www.ogorod.ru
How to distinguish by the type of leaves
First of all, when buying a seedling, the gardener should take a closer look at the leaves of the plant. Both the wild rose and the rose have quite spectacular and have an unusual structure. In both of these cultures, each leaf consists of a "twig" and several small leaves growing on it. Asking the question of how to distinguish a rose from a wild rose, the first step is to count the number of the latter. Rose hips have 7 leaves on each "twig". In a rose, their number never exceeds 5. Sometimes on the "branches" of this culture, 3 leaves grow. Also, in rose hips, the topmost leaf is usually unpaired.

The leaves of the rose have a very dark glossy color and are quite large. In rose hips, they are small, more delicate and matte. Also, the leaves of this plant have a pale green light color.
How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose by the type of shoots
On this basis, distinguishing plants is also not difficult. The rose shoots have a reddish color. Over time, they become woody and acquire a dark green color. The wild rose shoots are more tender. In addition, they initially have a light green color. If nothing red is noticeable on the seedling, it is most likely a wild rose.
Also, when buying a rose for planting, you should pay attention to the thorns of the bush. In roses, they are usually very long and rarely located. In rose hips, the spines are short and often distributed. Sometimes they even appear on the leaves and sepals of this plant.
The main distinguishing feature of a rose is its red shoots. The thorns of some varieties are also short, and the leaves are seven-petal. It is on the color of the shoot that you should first of all pay attention.

What to do if the rose turned into a dog rose
So, we figured out how to distinguish a rose from a wild rose by leaves and shoots when buying a seedling. But sometimes summer residents have problems with the "queen of flowers" even if she has already taken root on the site. The plant is tender and can easily freeze in winter. Often after this it happens that the shoots begin to grow "from the root." In this case, most often the rose turns into a wild rose. If the shoots go above the grafting site under the ground, the owners of the garden will again receive the "queen of flowers". Below the grafting site, only rosehip shoots sprout.
What to do if the rose has turned into a wild rose? In order to remedy the situation, garden owners just need to take a closer look at the bush. It often happens that along its edges a lot of wild rose shoots grow. In the middle, you can see a couple of rose branches. All that needs to be done in this case is simply to remove the rosehip.
It should be done correctly. If the rose has turned into a wild rose, it is worth cutting off unnecessary shoots by digging up the flower beds a little. Weed shoots are removed in this case right underground - at the very base. Otherwise, in the future, the rose will not look too neat, and the wild rose will begin to sprout again.
Sometimes rebirth also occurs due to improper selection of a stock or violation of planting technology. In this case, the rosehip shoots simply clog the rose shoots. It is necessary to plant the "queen of flowers" with a slight deepening of the grafting site.

Now you know how to distinguish a rose from a wild rose. Prune the first to prevent rebirth, usually twice a season. This method is, therefore, rather troublesome. It is much easier to immediately transfer the rose to “its roots”. Carry out this procedure in the spring, after thawing the soil. At the same time, a trench is dug from the trunk of the bush. Then they bend and fix one of the shoots in it. Subsequently, the branch will give roots and a new separate rose bush will appear in the garden.
You can use this method only for winter-hardy varieties of the "Queen of Flowers". A bush grown in this way will reach full decorativeness for 4-5 years.
www.kakprosto.ru
Rose and wild rose: what are the differences
The differences between a blooming rose and a wild rose are obvious:
- The rose has more decorative flowers with a large number of petals, the usual wild rose has exactly five of them. There are also decorative, terry varieties of wild rose, but they are inferior to the rose in decorativeness: smaller flowers and a pronounced core will not allow them to be mistaken for a rose.
- Rose hips bear fruit: in late summer and autumn, round or oval-shaped fruits filled with seeds appear on it. In wild varieties of wild rose, the fruits are dark red, in cultivated varieties - from orange to blue-black. The rose does not bear fruit.
- The leaves are also very different. The rose leaves are smooth, without pronounced veins, of an even dark green color. Rose hips are pubescent, sometimes with thorns, light green and uneven.
In addition, roses come in a wide variety of shades, wild rose hips are light pink, garden varieties also have white and cyclamen colors.
How not to make a mistake when buying seedlings
Unlike a flowering bush, the difference between rose and rosehip seedlings is not so obvious, and inexperienced gardeners can be sold an ordinary rosehip instead of the desired rose bush. How not to make a mistake when buying?
Firstly, it is necessary to clarify whether the rose seedling is grafted onto a wild rose or whether it is own-rooted. A grafted seedling in the lower part of the stem must have a thickening - the place of vaccination. The stem below the thickening may vary in color. Own-rooted roses have no place to graft. In order not to become a victim of fraud by unscrupulous sellers, own-rooted roses should be bought only in trusted nurseries or with buds.
There are 4 differences that will distinguish rose seedlings from wild rose:
- Young shoots of roses are dark red, gradually they turn green and woody. Rose hips, on the other hand, have bright green young shoots.
- There are three or five leaves on a leaf branch of a rose. There are seven leaves on a rosehip branch.
- The leaves of the rose are quite large, smooth, shiny, dark green in color. Rosehip leaves are lighter, smaller, have a pronounced structure and do not shine.
- The thorns of pink shoots are large and rarely located on the stem. Rosehip shoots are completely covered with small short thorns, there are also spines on the sepals and petioles of the leaves.
It should be noted that there are exceptions to these rules. Some varieties of spray roses with small flowers have 7 leaves per branch and rather small thorns. They are very decorative, although they look like wild roses, and, moreover, are unpretentious. Mature shoots of such roses are brown, flowers are of different shades depending on the variety.
The ability to distinguish a rose from a wild rose comes with experience, so you can seek help from specialists or experienced flower growers.
Rose lovers are familiar with such a problem when a rosehip grows instead of a rose bush after planting in the garden. It is very difficult for a non-professional to distinguish both plants from each other, because they belong to the same family. However, it is still possible to determine the substitution, if you know what to look for. How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose will be described in detail below.
The rose, like its close relative, belongs to the Rosaceae family. This fact explains why these two different plants are difficult to distinguish from each other, especially at the seedling stage.
Rose is a member of the genus Rosehip. So its very common on this bush. It was obtained through painstaking selection work of scientists from around the world. To date, this flower is represented by a variety of varieties, the flowers of which have both a different color of the petals and the structure of the inflorescences. To obtain such a huge variety, the method of multiple crossing was used. At the same time, some species are forms of wild rose hips. Therefore, both plants have a genetic and external similarity.
At the same time, it should be understood that a rose is a collective name that contains various representatives of this genus. Therefore, it is not surprising that novice flower growers often confuse these plants. General points here include:
- one family;
- some are considered a cultivated wild plant.
However, despite certain similarities, both plants have obvious differences. For example, rosehip, despite the external similarity, is different in that after flowering it forms a fruit that is very rich in vitamin C. According to this indicator, it even surpasses citrus fruits.
The main distinguishing characteristic of both cultures from other plants is the characteristic structure of the flower. It is bisexual and has a double perianth. The flower calyx has five fused sepals. The flowers themselves can be collected in inflorescences or located separately.
To distinguish a rose from its close relative, you need to know what to look for when buying a seedling for growing in the garden.
The main differences between rose and wild rose
The most common mistake novice flower growers who are going to breed roses is buying seedlings of a different kind. The main differences between these two closely related plants is the fact that they form different flowers. The differences here lie in the following:
- the rose has more decorative and beautiful flowers. Its flowers are characterized by a larger number of petals. Rosehip has five petals as standard;
- the fruit-forming relative blooms in small flowers, which may have a slight doubleness. However, in these parameters they are significantly inferior to the rose. Its flowers have a pronounced core;
- after flowering, rose hips form oval/round fruits. The fruits contain seeds inside. Wild varieties produce red fruits, while cultivated varieties are blue-black or orange. But roses (any variety) do not form fruits at all. After flowering, the petals from the bushes simply crumble;
- plants differ in the color of the petals. Rose hips are characterized by a light pink color. But roses can bloom in inflorescences of various colors: white, red, orange, pink, etc.
However, when buying seedlings, it is still impossible to evaluate plants by flower parameters. Therefore, here it is necessary to be guided by other parameters of the assessment. First, you should ask the seller if the bush has been grafted. Grafted plants have a slight thickening at the bottom of their shoot, which is the place of grafting. Below the thickening, the stem may acquire a different color.
It should be noted that own-rooted varieties of roses are not grafted. In this case, you need to rely on other parameters in which the rose differs.
In addition to the above points, a rose and a wild rose differ in leaves, shoots and thorns. Let us consider these parameters in more detail, since it is on them that attention is always focused when .
Leaves
You can tell one plant from another by its leaves. In roses, the leaf blade has a dark green color. At the same time, it has slightly rounded tips, leatheriness and density, as well as a shiny surface. Its leaves are larger. A rose has 3–5 leaves on a leaf branch, and a relative has 7 leaves.
Rosehip leaves are rough and dull. They usually have a light olive color. The leaf plate has a pointed tip. Edges may be uneven. Sometimes the leaves are characterized by pubescence and thorns.
shoots
The rose has young shoots of dark red color. Over time, they turn green and woody. But the shoots of the analogue are always bright green. They also form thinner.
Already on the basis of the differences between the leaves and shoots, you can determine which particular seedling they are trying to sell you.
spikes
Those who are not completely convinced by the leaves and stems should rely on such a parameter as thorns when choosing a seedling. Roses are characterized by rare, but rather large thorns. Therefore, they are considered more traumatic, although similar formations in a relative are no less dangerous. At the same time, wild rose shoots are completely strewn with short and small thorns. Here, thorns can be found not only on the stems, but also on the sepals and petioles. It is because of the abundance of spines that this plant got its name.
Despite the presence of such obvious differences, the rose still manages to pass itself off as a wild rose and vice versa. Such confusion is connected with the fact that the distinctive characteristics of these plants can be smoothed out to a certain extent by multifaceted selection work. And only a true professional can distinguish one culture from another.
When growing roses, remember that improper care can provoke the degeneration of bushes in the direction of an ordinary wild rose.
Video "How to distinguish a rose from a wild rose"
From this video you will learn how to quickly distinguish a rose from a wild rose.









